One of the key aspects of flange design is the flange face, which directly affects the sealing performance of the flange joint. The selection of a flange face depends on the pressure, temperature, and maintenance requirements. In this article, you will learn about the various flange faces available for selection such as.
Table of Contents
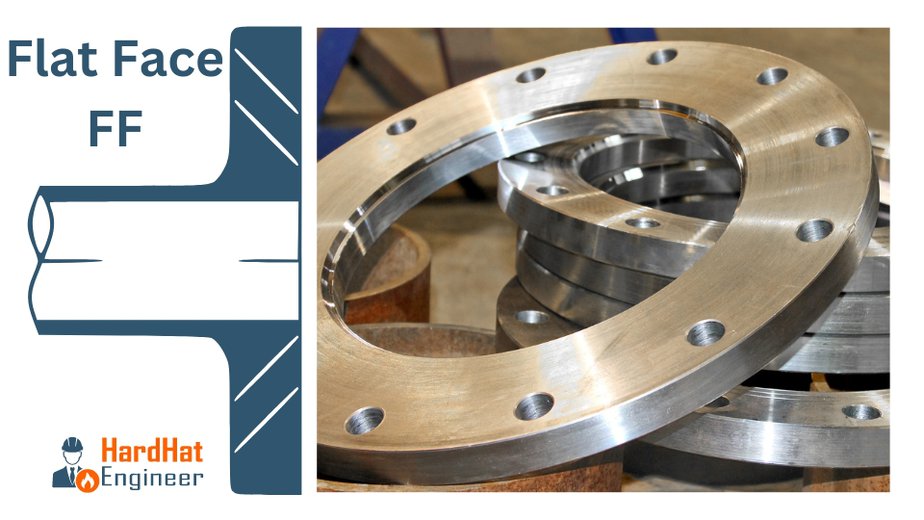
Flat Face – FF Flange
As the name suggests, the flat face (FF) flange has a flat face. Flat face flanges are used when the counter-flanges are flat faces. This condition occurs mainly in connection to Cast Iron equipment, valves, and specialties. A full-face gasket is used when a flat face flange is used.

Key Characteristics:
- The entire face of the flange is flat as shown in the image above.
- Used primarily in systems where cast iron or fiberglass is used, to avoid bending or cracking.
- The gasket type used with FF flanges is usually a full-face gasket.
Advantages:
- Simplifies alignment during installation due to the flat surface.
- Ideal for low-pressure, low-temperature applications.
- Reduces the risk of flange warping or cracking under bolt pressure.
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for high-pressure applications because it lacks the ability to provide a high-integrity seal.
- Prone to leakage if not properly aligned.
Common Applications:
- Low-pressure water piping systems.
- Non-critical service applications where high sealing integrity is not required.
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
Raised Face – RF Flange
Raised face flange has a small portion around the bore raised from the face. The gasket seat on this raised face. The height of the raised face depends on the flange pressure-temperature rating, known as a flange class.
For 150# & 300# height of the raised face is 1/16”, and above 300#, it is 1/4”. The inside bore circle type of gasket is used with a raised face flange.
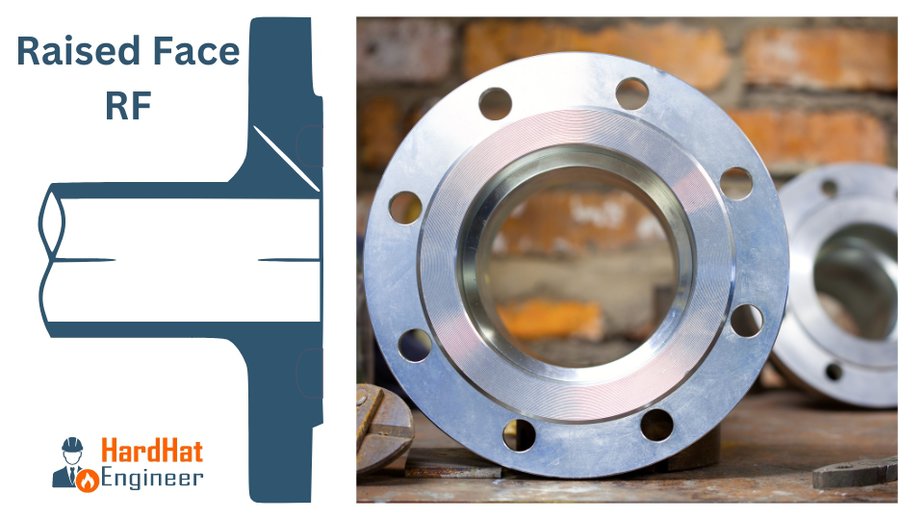
Key Characteristics:
- The raised portion is the only area that comes in contact with the gasket.
- Available in two raised face heights: 1/16 inch for lower pressure classes (150 and 300) and 1/4 inch for higher pressure classes (400 and above).
Advantages:
- Improved sealing capability due to the raised face.
- Suitable for a wide range of pressures and temperatures.
- Allows for the use of different gasket types, such as spiral wound or cam profile gaskets.
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than flat face flanges due to the additional machining.
- Requires careful alignment to ensure proper sealing.
Common Applications:
- Oil and gas, Petrochemical and chemical processing plants Piping.
- High-pressure and high-temperature services.
RTJ Face – RTJ Flange
Ring joint type face flange has a specially designed grove in which metal gasket seats. This type of flange is used in high pressure and temperature services with metalic gasket.
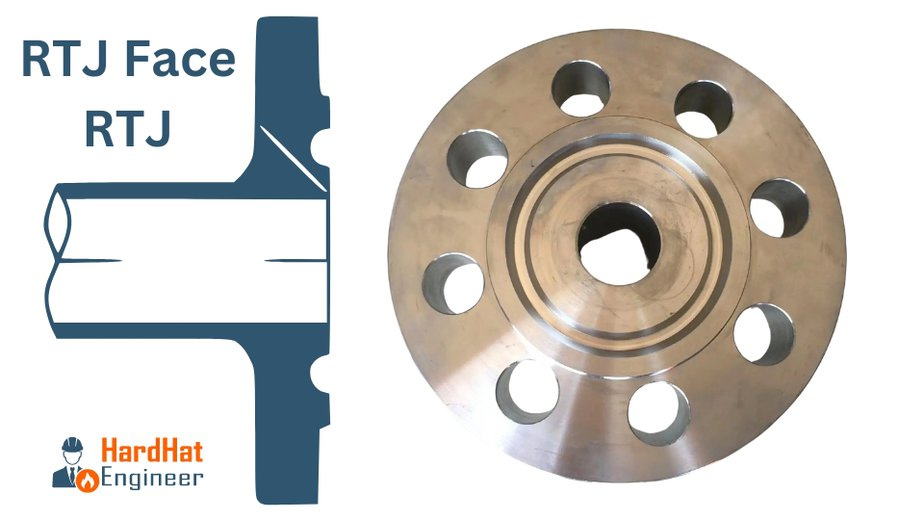
Key Characteristics:
- A machined groove on the flange face where a metal ring gasket is seated.
- Provides a very strong and leak-proof metal-to-metal seal.
- Suitable for harsh environments where high pressure and temperatures are common.
Advantages:
- Exceptional sealing capabilities, especially under high pressure and temperature.
- Reduced risk of gasket blowout or leakage.
- Metal-to-metal contact provides a durable and long-lasting seal.
Disadvantages:
- Requires specialized gaskets and precision machining, increasing cost.
- More challenging to install and align compared to other flange types.
Common Applications:
- High-pressure pipelines, such as those found in the oil and gas industry.
- Offshore drilling and subsea applications.
Tongue and Groove (T&G) Flange
Tongue and Groove (T&G) flanges have a matching tongue (raised) and groove (depressed) on opposing flange faces. This design helps to ensure proper alignment and provides additional support for the gasket, enhancing the seal’s reliability.
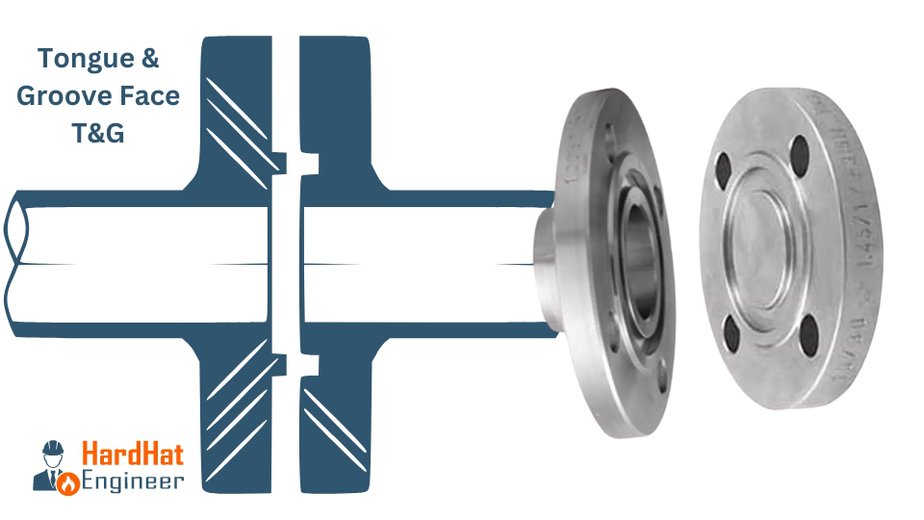
Key Characteristics:
- The tongue (raised portion) on one flange fits into the groove (depressed portion) on the other flange.
- Designed for easy alignment and excellent sealing properties.
- Gaskets are typically placed in the groove, protecting them from the external environment.
Advantages:
- Provides a self-aligning feature, making installation easier.
- Reduces gasket movement during assembly, enhancing the seal’s integrity.
- Suitable for both moderate and high-pressure applications.
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than flat face or raised face flanges due to the complexity of the design.
- The design is specific and requires matched pairs for proper alignment.
Common Applications:
- High-pressure steam and water systems.
- Services requiring a tight seal with minimal gasket deformation.
Male and Female Flange
Male and Female flanges feature a raised portion (male) on one flange face and a corresponding recessed area (female) on the mating flange. The male face fits into the female face, providing a tighter, more secure connection.
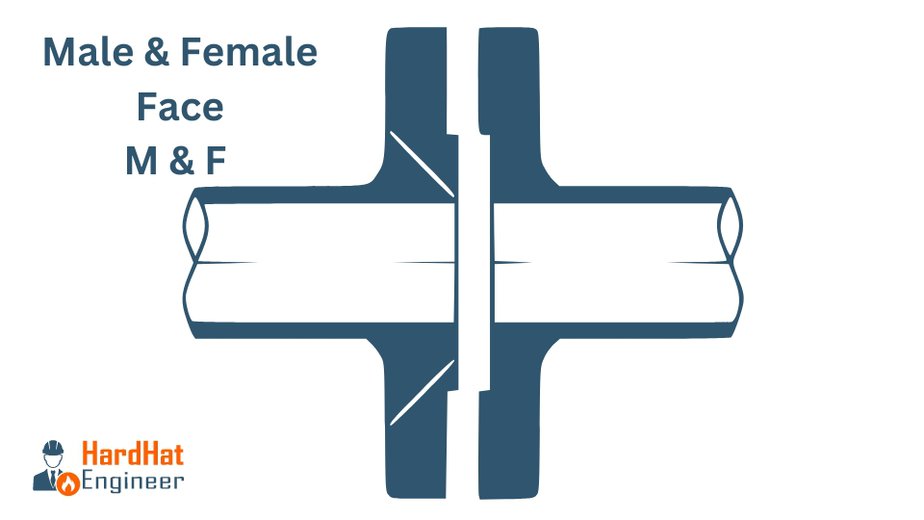
Key Characteristics:
- The male face has a raised ring, while the female face has a matching depression.
- Designed for use with soft iron gaskets or other metallic gaskets that deform slightly to fill any gaps.
Advantages:
- Excellent sealing capabilities due to the precise fit of the male and female faces.
- Suitable for moderate to high-pressure applications.
- Reduces the risk of gasket extrusion and blowout.
Disadvantages:
- Requires precise alignment during installation to ensure a proper seal.
- Limited compatibility with standard flanges due to the specific design.
Common Applications:
- Use in Heat Exchanger shell to bonnet joint.
- Specialized equipment in the oil and gas industry.
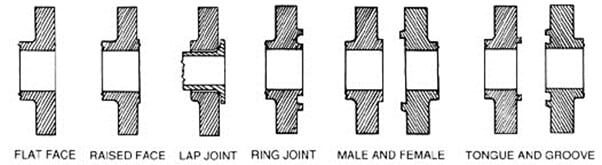
Comparison of FF, RF and RTJ Face
In the image below, you can see side by side comparison of Flat Face, Raised Face and RTJ Face Flange.

Flange and Olet Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz