What is Plug Valve?
A plug valve is a Quarter-turn rotary motion Valve that uses a tapered or cylindrical plug to stop or start the flow. The disk is in plug shape, which has a passage to pass the flow.
This bored passage is in line with the flow in the open position. When the plug is turned 90° from the open position, the solid part of the plug blocks the flow.
It is used in place of a gate valve where quick operation is required. It can be used in high-pressure temperature services.
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
Types of Plug Valves
These valves are available in either a lubricated or non-lubricated design and with different styles of port openings through the plug.
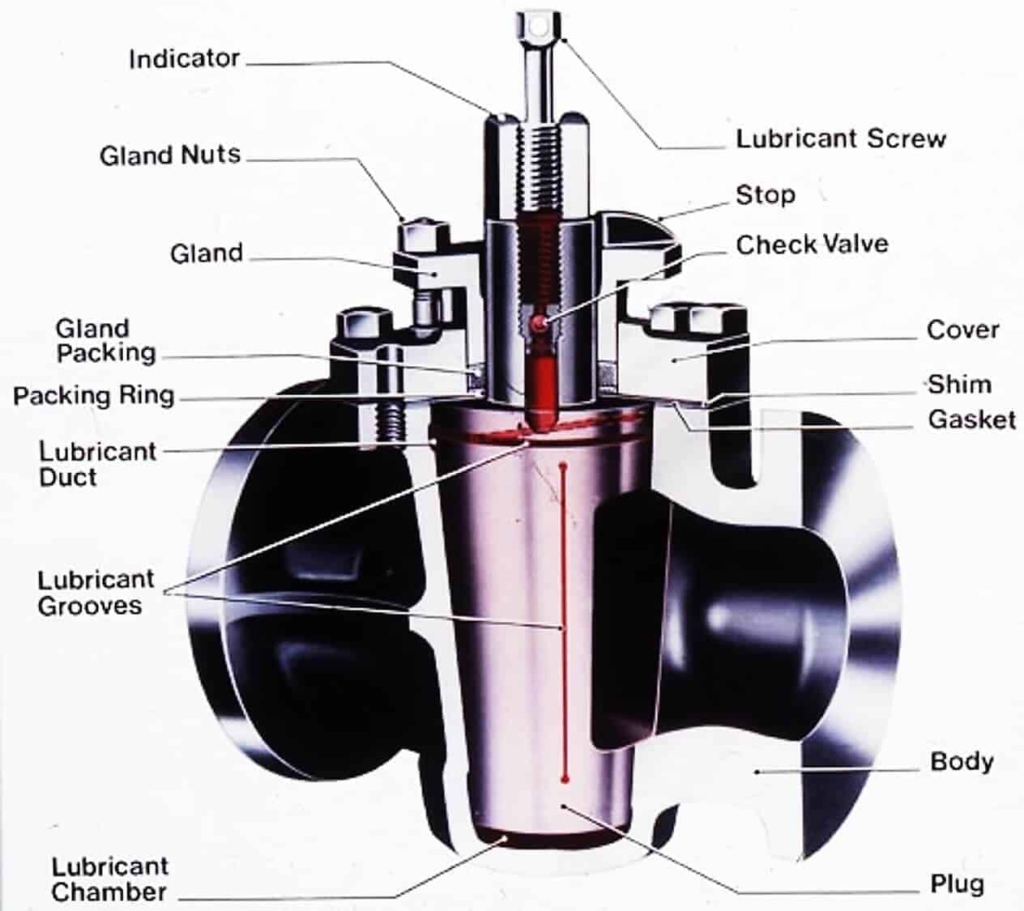
Lubricated Plug Valve
The plug inside a lubricated plug valve has a cavity in the middle along its axis. You can see this in the image. The lubricant chamber at the bottom and the sealant injection fitting at the top ensure the supply of lubricant.
The small check valve below the injection fitting prevents the sealant from flowing in the reverse direction once the sealant is injected into the cavity.
The plug surface gets constantly lubricated by the sealant that moves from the center cavity through radial holes into lubricant grooves on the plug surface. Now, why are we required all this? Many plug valves are of all-metal construction.
The narrow gap around the plug may allow leakage, and if you reduce the gap further, it will increase the friction, and the plug may get stuck inside the valve body.
Image – Serck Audco, Newport
The lubricant reduces the force required to open or close the valve and allows smooth movement of the plug. It also prevents corrosion of the plug.
The lubricant material must be compatible with the fluid of the pipeline. It should not dissolve or wash away by the flow medium as this could contaminate the fluid and damage the seal between the plug and the body, resulting in leakage. Also, the sealant used must be able to withstand the temperature of the flow medium.
Lubricated plug valves are available in the large size range and fit to work in high-pressure temperature services. These valves are subject to less wear and provide better corrosion resistance in some service environments.
Valve Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
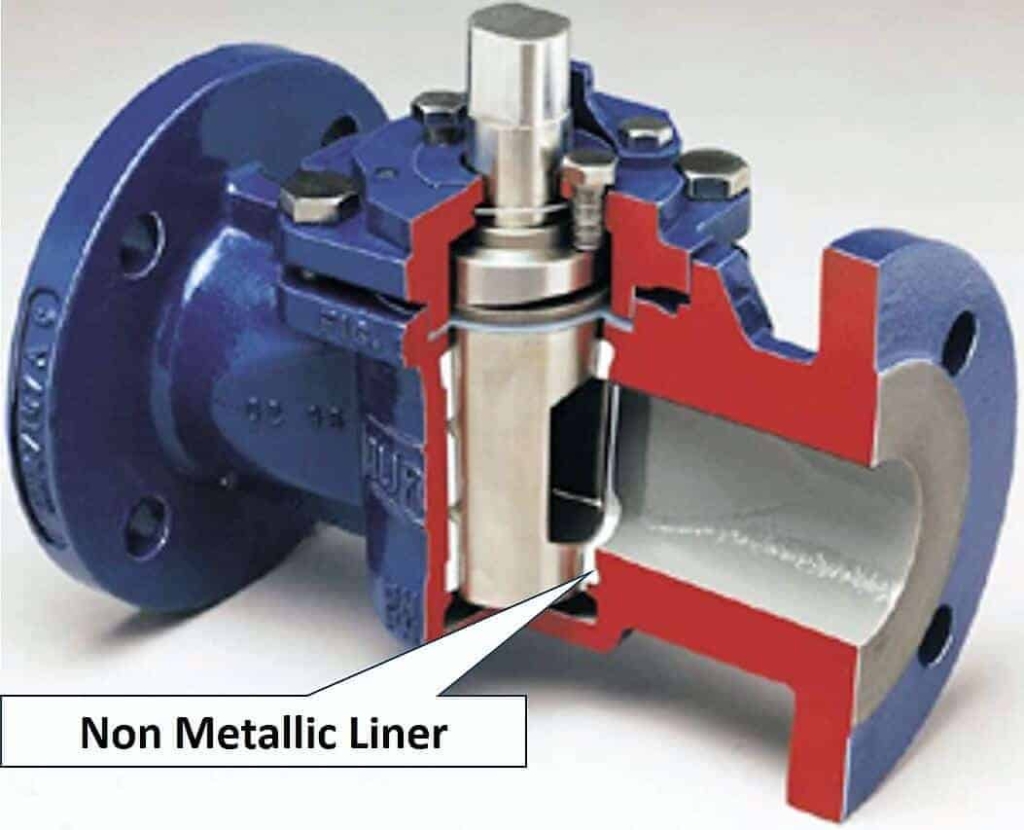
Non-lubricated Plug Valves
A non-metallic elastomeric sleeve or liner is used in this type of valve. This sleeve is installed in the body cavity of the valve. The polished tapered plug acts as a wedge and presses the sleeve against the body.
This nonmetallic sleeve reduces the friction between the plug and the valve body. Non-lubricating plug valves required minimum maintenance. Due to the non-metallic seat, these valves are not used in high-temperature services.
Lubricating and non-lubricating valves are capable of providing a bubble-tight shutoff and are of compact size.
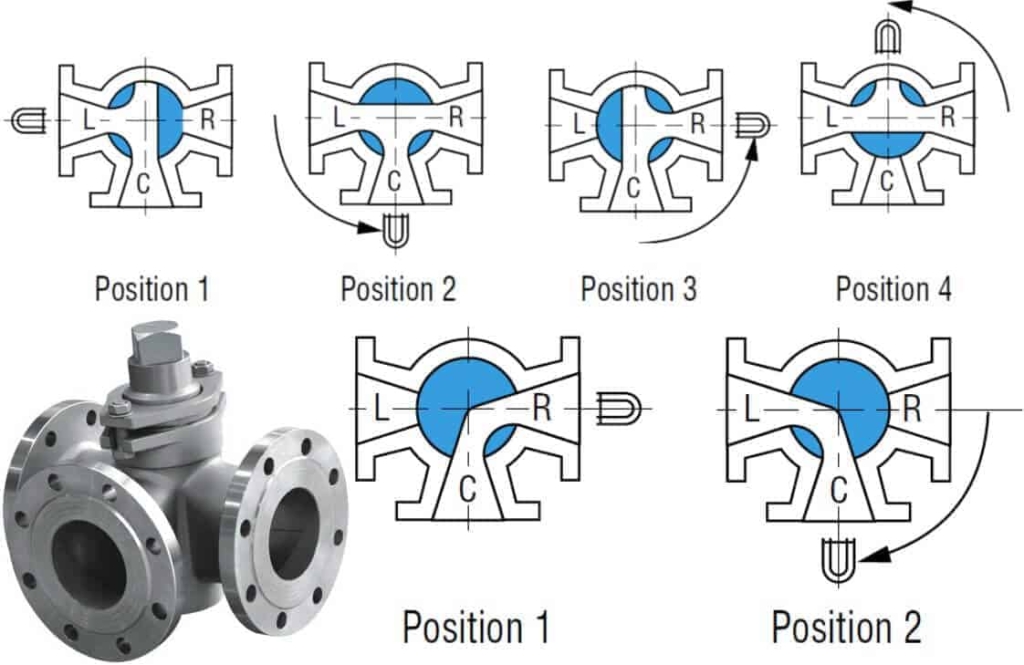
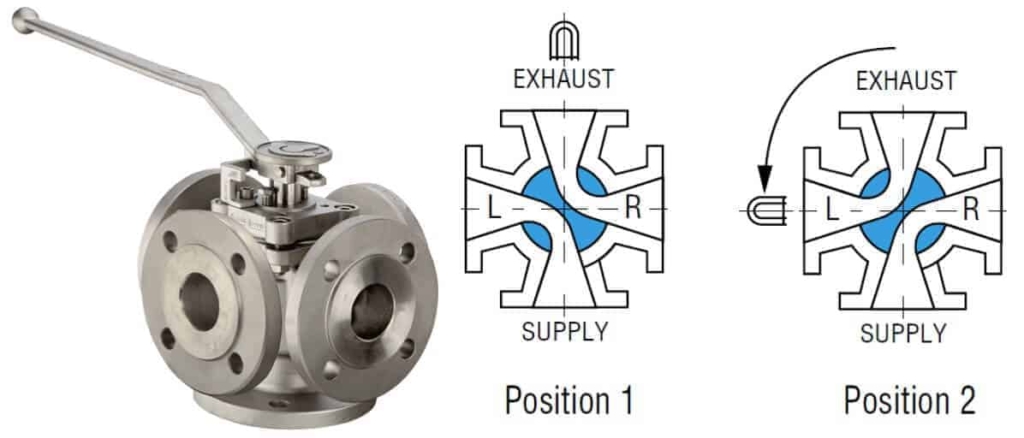
Multi-Port Plug Valves
Here you can see the 3-way multiport plug valve. The top image is of 3-way 3-port design, and the bottom is a 3-way 2-port design.
The image below shows a 4-way design.
Multiport valves are used in transfer lines and for diverting services. A single multiport valve may serve the purpose of three or four gate valves or other types of shutoff valves.
However, sometimes the multiport valve does not completely shut off flow. Great care should be taken in specifying the particular port arrangement for proper operation.
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
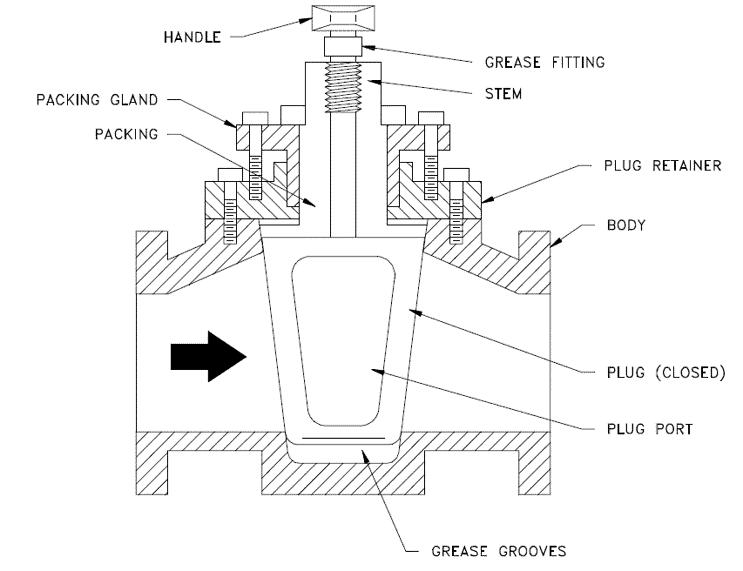
Plug Valve Parts
The typical plug valve is consisting of a body, bonnet, stem, and plug. The seat is an integral part of the body in the case of a lubricated type. For a non-lubricated type, a non-metallic seat is used to improve the leak tightness of the valve.
Image- DOE Handbook
Plug Valve Disk Types
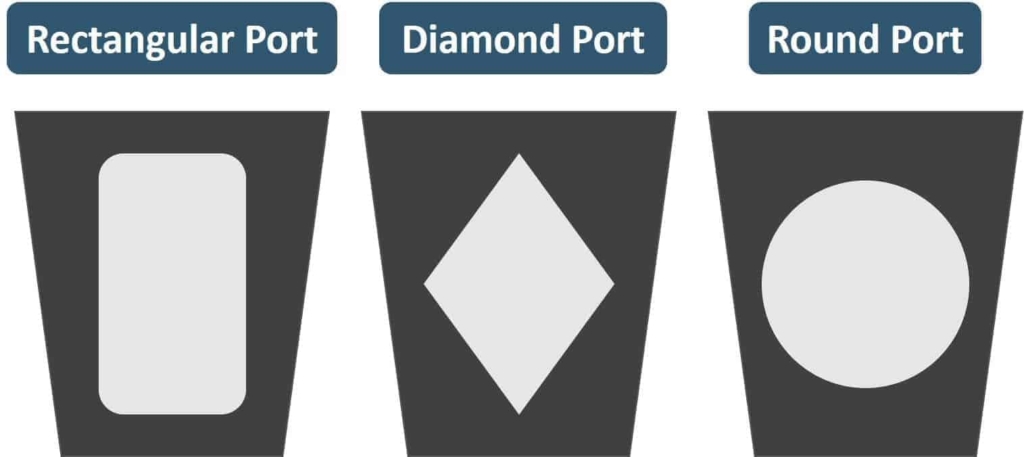
Plugs are either round or taper cylinders. They may have various types of port openings, each with a varying degree of the opening area.
Plugs are available with
- Rectangular Port
- Round Port and
- Diamond Port
Here in the image, you can see the taper plug with Rectangular, Round, and Diamond Port designs.
P&ID Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz
- Rectangular Port is the most common for a plug valve. The rectangular port represents at least 70% of the corresponding pipe’s cross-sectional area.
- The round port plug has a round opening through the plug. It is available in full bore and reduced bore designs. Valves with reduced ports are used only where restriction of flow is not important.
- The Diamond Port plug has a diamond-shaped port through the plug. All diamond port valves are venturi restricted flow types. This design is for throttling service.
Application of Valve
- This valve is used as an on-off stop valve and is capable of providing a bubble-tight shutoff.
- It can be used in different types of fluid services such as Air, gaseous, vapor, Hydrocarbon, slurries, mud, and sewage applications.
- Also used in a vacuum and high-pressure & temperature applications
Advantages
- Simple design with few parts
- Quick to open or close
- inline maintenance possible
- Offers minimal resistance to flow
- Provides reliable leak-tight service
- Multiple port design helps reduce the number of valves needed and permits a change in a flow direction.
Disadvantages
- It requires greater force to operate due to high friction
- Larger valves cannot be operated manually and require an actuator
- Pressure drop due to reducing port
- The cost of Plug valves may be more than ball valves for a given size and class.
Click here to learn about Other Types of Valve.
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses