In this article, I am going to explain to you about the cavitation in Centrifugal Pump. You will learn about;
- What is cavitation?
- Reasons for cavitation
- How to prevent cavitation.
If you don’t want to read this article, you can watch the video below explaining the pump cavitation in detail.
What is Cavitation?
What is cavitation? Why do you have to know about it? Have you ever seen the pump that makes a sound like it is transporting marble and gravel? Well, cavitation is responsible for such a high sound and vibration in the pump.
When vapor bubbles are created inside the pump and subsequent collapsing of these bubbles inside the pump is known as cavitation. Collapsing of bubbles creates tremendous pressure jet and shockwave inside the pump. This will result in high noise and vibration in a pump.
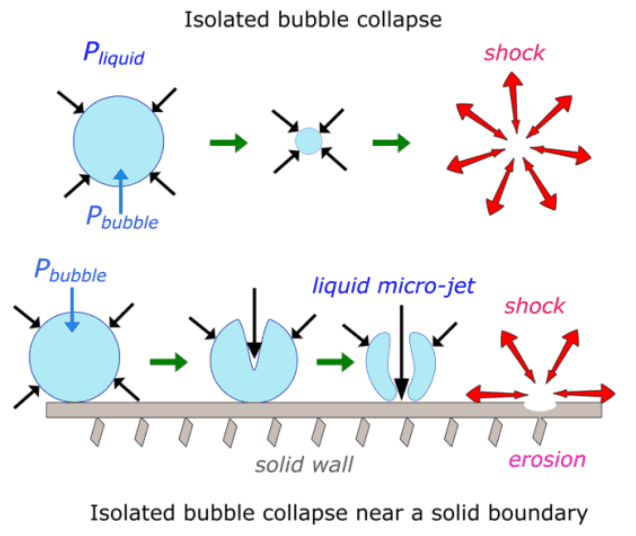
Image Source–
Prasanta Sarkar, Giovanni Ghigliotti, Marc C. Fivel, Jean-Pierre Franc. Numerical investigation of the dynamics of pressure loading on a solid boundary from a collapsing cavitation bubble. 10th International Symposium on Cavitation – CAV2018, May 2018, Baltimore, United States. HAL-02066205
There are many reasons for vapor bubble creation. I will explain the same to you in a minute. First, look at the image shown here. It shows collapsing of bubbles near-surface and away from the surface.
When the vapor bubble collapses far from the surface, as shown here, it will create a shock wave inside the liquid. And when vapor collapse near the surface, the pressure jet hits the surface with pressure in the range of ten thousand to fifteen thousand PSI. Yes, that is in the range of 10 to 15 thousand PSI range. This will create a pit and erode the surface.
Centrifugal Pump Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz
Damage by Cavitation
This will damage the surface of the impeller or pump housing. Damage done by such bubbles is shown here in the photos. You can see that harmless and soft bubbles can make your pump completely out of service.

Image Source – Rodelta & Wikimedia
We all know that when liquid gets boiled, vapor bubbles start appearing in the liquid. But how does liquid get boiled in the pump? Each liquid has its boiling point. If you reduce the pressure, the boiling point gets lowered, and if you increase the pressure, the boiling point gets higher.
What does that mean? Liquid start boiling at a lower temperature if you reduce the pressure. The same thing happens inside the pump when pressure falls below the liquid’s vapor pressure. It starts boiling and creates vapor bubbles. When the bubbles reach the higher-pressure zone within the pump, it gets collapsed.
You can easily identify whether a pump is cavitating by the sound it makes. If you listen to sound that makes you think that gravels are getting pumped, that is a clear sign of cavitation. Other than this, high vibration is also an indicator of cavitation.
Now you know cavitation. You should also know why cavitation happens in a pump. There are five main reasons that lead to cavitation in the pump.
Why does Cavitation Happen in Centrifugal Pump?
- Vaporization of liquid in a pump
This is the biggest reason for cavitation. As explained earlier, if the pressure inside the pump falls below the vapor pressure, the liquid starts boiling and creating vapor. To do this, you must keep enough head at the pump suction. As a thumb rule, NPSH Available should be 3 ft more than the NPSH required.
Now, the second reason for cavitation inside the pump is
- Recirculation
Recirculation in the pump happens when the discharge is restricted. When a liquid cannot exit the pump, it starts recirculation in the pump. This will lead to rising in the temperature of the liquid and the creation of a vapor bubble.
The third reason is
- The improper gap between impeller and pump housing.
If the gap between the impeller and pump housing is very low, it will lead to cavitation when the liquid passes through this gap at a high velocity.
- Air Ingress
If a pump is running at lower than atmospheric pressure, there is a chance of air ingress in the pump from any poor point. This air will create the same cavitation effect in the pump.
The last reason for the cavitation is turbulence in the flow.
- Turbulence or vortex occurs in the flowing liquid due to various design-related reasons in the piping system. If this vortex is getting formed near pump suction, it will have the same effects as vaporization or low NPSH.
There may be other reasons, but these five are the major contributor.
You can check the full course available on my website to learn more about the centrifugal pump principle, operation, and design. It is 7 hours long course covering every aspect of the Pump that will make you super confident about a centrifugal pump.
You can see some of the potential problems that come with prolonged cavitation in the pump.
- Vibration
- Noise
- Low efficiency
- Reduction in flow rate and head
- Physical damage to the impeller, pump housing
- Leaking of pump seal
- Problem with alignment
How to prevent cavitation in the pump?
Well, there are many things that help to avoid or minimize the cavitation in a centrifugal pump.
- Make sure the pump has enough head at suction. As said, your NPSH available at pump suction should be more than your NPSH required with enough safety margin. This will ensure that no vaporization will occur at the pump suction.
- Proper design of pump impeller so that clearance between pump housing and impeller will be good enough to avoid heating of the liquid.
- Don’t run the pump with a restricted flow to avoid recirculation.
- If the pump is running below the atmospheric pressure, make sure that there is no air ingress.
- Proper pumping system design will help you avoid vortex and prevent air accumulation at suction. For example, using eccentric reducer with flat side top as shown here.
Centrifugal pump cavitation is a big and complex topic. Pump manufacturers spend lots of time and money to achieve the best pump performance. What you have learned here will give you a good understanding of this topic.
You can check the full course available on my website to learn more about the centrifugal pump principle, operation, and design. It is 7 hours long course covering every aspect of the Pump that will make you super confident about a centrifugal pump.
Are You Piping Components Master?