In this article, I will explain to you about flange ratings. In definition, you can say that it is a combination of pressure class and temperature class. Or simply, it is the ability of the flange to withstand pressure at a given temperature. I have covered the following topics in this article to explain this.
- Definition of Pressure-Temperature Rating
- What is Temperature Rating?
- What is Pressure Rating?
- Flange Rating Equation
- Flange Class
While working with ASME/ANSI Flange, the terms such as Flange Ratings, Flange Pressure Ratings, Flange Class, and pressure-temperature rating of flanges are quite confusing. In this article, I have tried to simplify these terms to better understand young engineers.
What is a Pressure-Temperature rating?
Pressure- temperature rating is the maximum allowable non-shock gauge pressure at the specific temperature for a given material. I know it is still confusing. Let me further break this term.
ASME B16.5 is a standard for Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings that covers flanges sizes from NPS ½” to 24”. In this standard, flanges are classified based on their pressure-temperature rating, also known as a flange class.
What is a Flange Rating?
As per ASME B31.3, ratings are the maximum allowable working gauge pressure at the given temperature and pressure class for applicable material.
Temperature Rating
Piping materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel have different mechanical and chemical properties. The same material can handle different amounts of stress at different temperatures. Based on the ability of a material to handle the stresses at a given temperature, ASME B31.3 has devolved the maximum allowable stress value of the material at a specific temperature and is listed in Table A1.
In short, the reason behind establishing the temperature rating is to calculate the adequate wall thickness of the pipe, flange, and flanged fittings so that they can withstand the stresses due to pressure and other loads.
Flange and Olet Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
Pressure Rating
The pressure rating is safe working or maximum operating pressure with respect to the working temperature. It depends on the materials’ Stress-Strain characteristics. It is available in different Codes and Standards.
Flange Ratings
ASME B16.5 has listed the Pressure-Temperature ratings for flanges. These ratings are established based on the prime factor of hydro testing of the flanged fittings to the bursting and by adding a factor of safety of 3.0 at the rated working pressure and ambient temperature.
ASME/ANSI B16.5 has established these temperature-pressure ratings by using the formula given below and listed in the tabular form for all materials at different flange ratings.
PT = (Pr x SI) / 8750
- PT = rated working pressure in psig for specified material at temperature T.
- Pr = Pressure rating as per Class in Psig.
- SI = Selected stress in Psig for specified material at Temperature T.
- Refer to ASME B16.5 Annex B for the detailed calculation of Pressure Ratings.
Refer to the sample table below;
| Flanges pressure rating in psig for common carbon steel ASME flanges ( A105 / A350 LF2 / A350 LF3 / A350 LF6) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (F°) | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
| -20 to 100 | 285 | 740 | 985 | 1480 | 2220 | 3705 | 6170 |
| 200 | 260 | 680 | 905 | 1360 | 2035 | 3395 | 5655 |
| 300 | 230 | 655 | 870 | 1310 | 1965 | 3270 | 5450 |
| 400 | 200 | 635 | 845 | 1265 | 1900 | 3170 | 5280 |
| 500 | 170 | 605 | 805 | 1205 | 1810 | 3015 | 5025 |
| 600 | 140 | 570 | 755 | 1135 | 1705 | 2840 | 4730 |
| 650 | 125 | 550 | 730 | 1100 | 1650 | 2745 | 4575 |
| 700 | 110 | 530 | 710 | 1060 | 1590 | 2655 | 4425 |
| 750 | 95 | 505 | 675 | 1015 | 1520 | 2535 | 4230 |
| 800 | 80 | 410 | 550 | 825 | 1235 | 2055 | 3430 |
| 850 | 65 | 320 | 425 | 640 | 955 | 1595 | 2655 |
| 900 | 50 | 230 | 305 | 460 | 690 | 1150 | 1915 |
| 950 | 35 | 135 | 185 | 275 | 410 | 685 | 1145 |
| 1000 | 20 | 85 | 115 | 170 | 255 | 430 | 715 |
The above table shows that in a 150 lb carbon steel flange, the allowable pressure is 285 psi at 100°F, 170 psi at 500°F, and 20 psi at 1000°F. The only temperature at which the flange is rated for 150 psi is near 500°F. Higher class flanges are rated at their nominal pressure rating only at near 850°F. See the cells in yellows.
Flange Class
ASME has developed a flange Class considering temperature and pressure rating. There are seven Class 150#, 300#, 400#, 600#, 900#, 1500#, and 2500#.
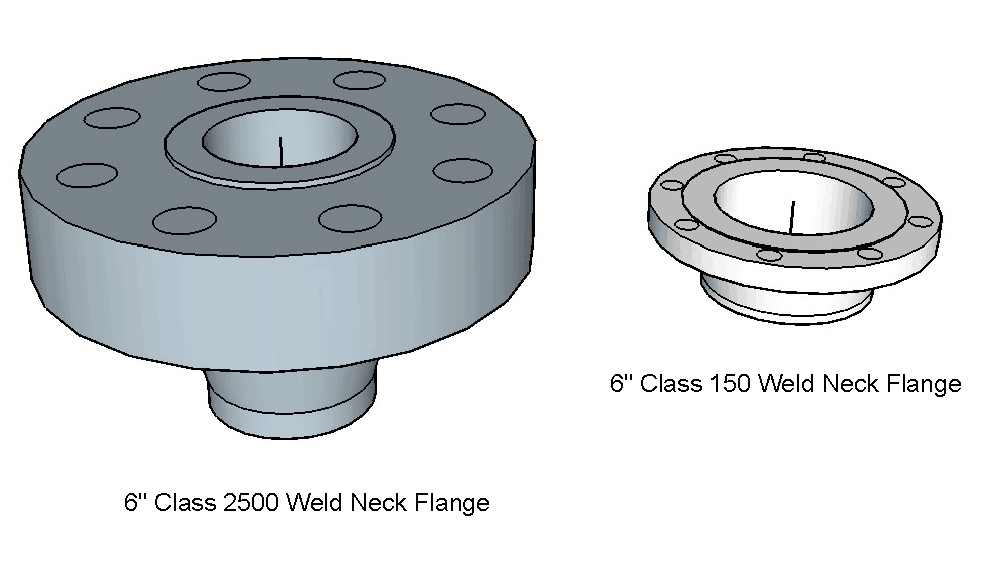
The higher the flange ratings, the heavier the flange and can withstand higher pressure and temperature. So, when the temperature goes up for a given material, the maximum allowable pressure goes down, and vice versa. See below for a comparison of 6” Class 150 and Class 2500 weld neck flange.
Now, these pressure classes of flanges are commonly known as “pounds” rather than “pounds per square inch.” Also, note that while describing the pressure class of flanges, terms such as “pound” and “class” may be considered interchangeable.
What is ASME / ANSI 150 pressure rating?
People refer to the same flange in different ways. For example, when we say class 150 flange, it means that the safe working pressure for this flange at the rated temperature for a given material is 150 pounds per square inch. See below some of the common ways to refer to the 150 Class flange
- Class #150 flange
- 150-pound flange
- class 150 flange pressure rating
- 150 pressure rating flange
- 150 lb flange
- Class flange ratings
How to determine flange ratings?
Well, it is very simple. Let’s assume that we want to use the ASTM A105 flange for our service, which has a pressure rating of 1,200 PSIG and at 500 °F.
| Flanges pressure rating in psig for common carbon steel ASME flanges ( A105 / A350 LF2 / A350 LF3 / A350 LF6) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (F°) | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
| -20 to 100 | 285 | 740 | 985 | 1480 | 2220 | 3705 | 6170 |
| 200 | 260 | 680 | 905 | 1360 | 2035 | 3395 | 5655 |
| 300 | 230 | 655 | 870 | 1310 | 1965 | 3270 | 5450 |
| 400 | 200 | 635 | 845 | 1265 | 1900 | 3170 | 5280 |
| 500 | 170 | 605 | 805 | 1205 | 1810 | 3015 | 5025 |
| 600 | 140 | 570 | 755 | 1135 | 1705 | 2840 | 4730 |
| 650 | 125 | 550 | 730 | 1100 | 1650 | 2745 | 4575 |
| 700 | 110 | 530 | 710 | 1060 | 1590 | 2655 | 4425 |
| 750 | 95 | 505 | 675 | 1015 | 1520 | 2535 | 4230 |
| 800 | 80 | 410 | 550 | 825 | 1235 | 2055 | 3430 |
| 850 | 65 | 320 | 425 | 640 | 955 | 1595 | 2655 |
| 900 | 50 | 230 | 305 | 460 | 690 | 1150 | 1915 |
| 950 | 35 | 135 | 185 | 275 | 410 | 685 | 1145 |
| 1000 | 20 | 85 | 115 | 170 | 255 | 430 | 715 |
Now refer to the pressure-temperature table for carbon steel flanges given above. Flange with 600# rating meets the requirement. You can see that Class 600# can withstand 1205 Psig pressure at 500 °F. See the cell highlighted in Green.
The information listed in this article is based on my research on the topics and may not be 100% correct. Any correction is welcome.