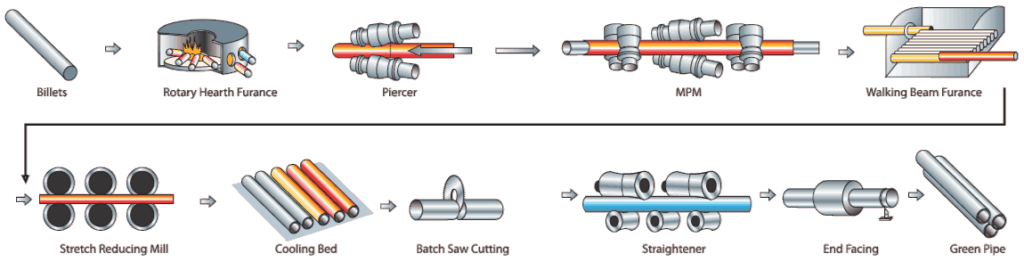
Seamless Pipe Manufacturing Process
Seamless pipe is the strongest among all pipes type as it has a Homogeneous structure throughout the pipe length.
- Seamless pipes are manufactured in a variety of sizes and schedules. However, there is a Restriction on the manufacturing of large-diameter pipes. Seamless pipes are widely used in manufacturing pipe fittings such as bends, elbows, and tees.
- Various Manufacturing processes are explained in detail;
Mandrel Mill Process
In the Mandrel Mill pipe manufacturing process, the steel billet is heated to a high temperature in the rotary furnace. A cylindrical hollow, also known as a mother hollow, is produced with the help of a rotary piercer and a set of roller arrangements that keeps the piercer at the center of the billet.
The outside diameter of the piercer is approximately that of the inside diameter of the finished pipe. With the help of a secondary roller arrangement, outside diameter and thickness are achieved.
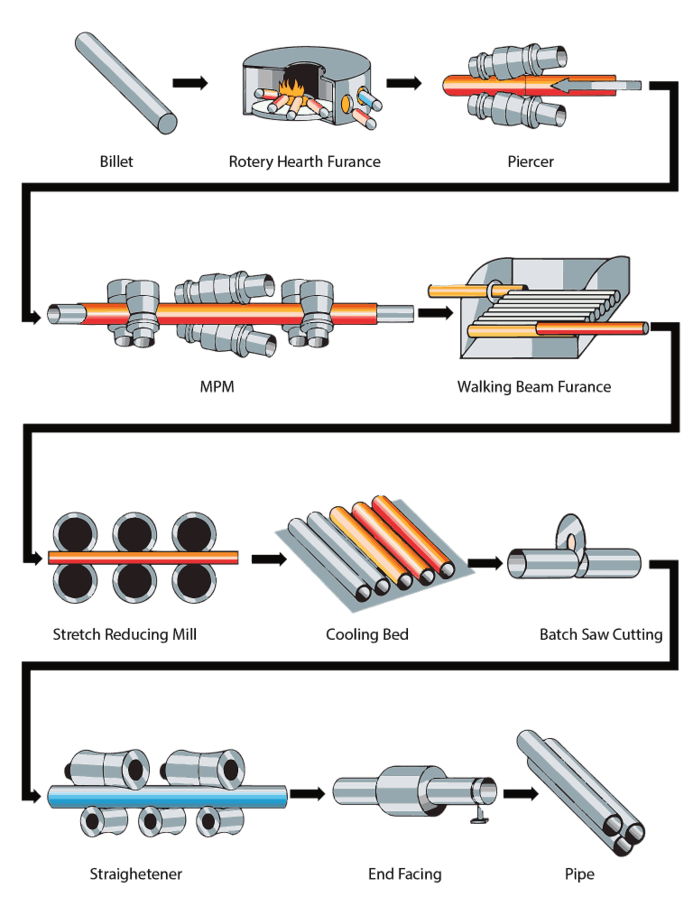
Mannesmann Plug Mill Pipe Manufacturing Process
Mannesmann was a German engineer who invented this pipe manufacturing process. The only difference between the Plug mill process and the Mandrel mill process is that in the mandrel method, inside diameter is achieved in a single pass. In contrast, in Mannesmann, a multi-stage reduction is possible.
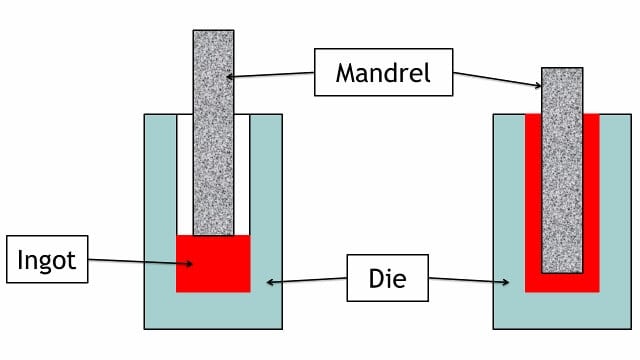
Forged Seamless Pipe Manufacturing Process
In a Forging pipe manufacturing process, a heated billet is placed in a forging die with a diameter slightly larger than the finished pipe. A hydraulic press of forging hammer with matching inside diameter is used to create cylindrical forging.
Once this forging is done pipe is machined to achieve the final dimension. The forging pipe manufacturing process is used to manufacture large-diameter seamless pipes that cannot be manufactured using traditional methods. Forged pipes are normally used for the steam header.
Piping Component Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
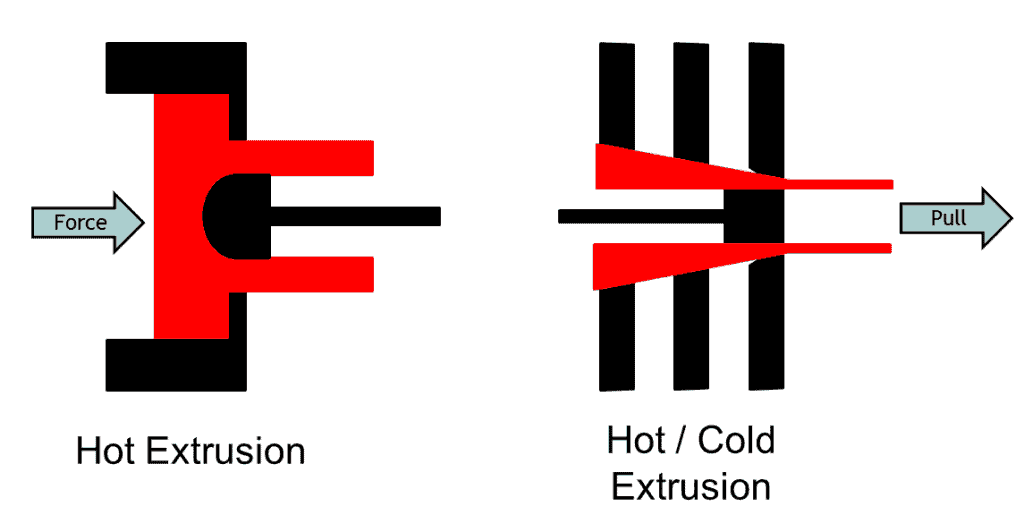
Extrusion Processes
In extrusion pipe manufacturing, a heated billet is placed inside the die. A hydraulic ram pushes the billet against the piercing mandrel, and material flows from the cylindrical cavity between the die and mandrel. This action produces the pipe from the billet.
Sometimes, manufacturers produce a high-thickness pipe known as mother hollow. Many secondary pipes manufacturers used this mother hollow to produce pipes with different dimensions.
Welded Pipe Manufacturing Process
Welded Pipes are manufactured from Plate or continuous Coil or strips. To manufacture a welded pipe, the first plate or coil is rolled in the circular section with the help of a plate bending machine or a roller in the case of a continuous process.
Once the circular section is rolled from the plate, the pipe can be welded with or without filler material. A welded pipe can be manufactured in large sizes without any upper restriction. Welded pipe with filler material can be used to manufacture long-radius bends and elbows.
Welded pipes are cheaper than the seamless pipe and are weak due to the weld.
There are different welding methods used to weld the pipe.
- ERW- Electric Resistance Welding
- EFW- Electric Fusion Welding
- HFW- High-frequency welding
- SAW- Submerged Arc Welding (Long seam & Spiral Seam)
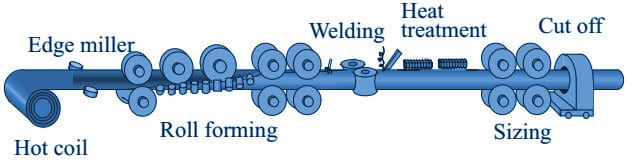
ERW Steel Pipe Manufacturing Process
In the ERW / EFW / HFW pipe process, the first plate is formed in a cylindrical shape, and the longitudinal edges of the cylinder formed are welded by flash-welding, low-frequency resistance-welding, high-frequency induction welding, or high-frequency resistance welding.
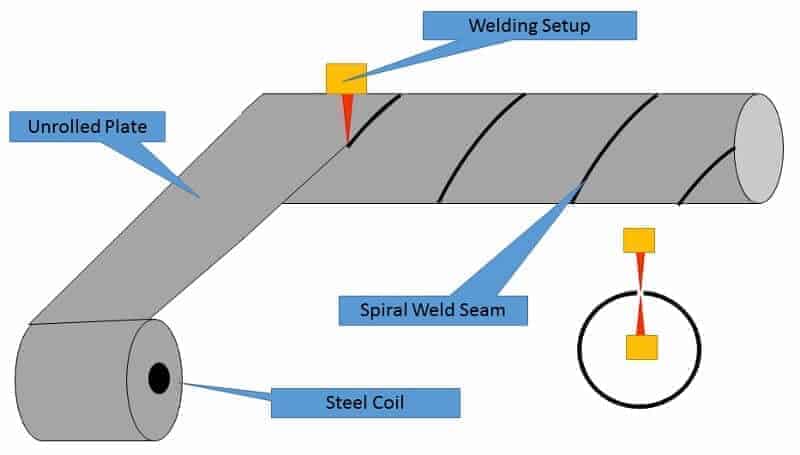
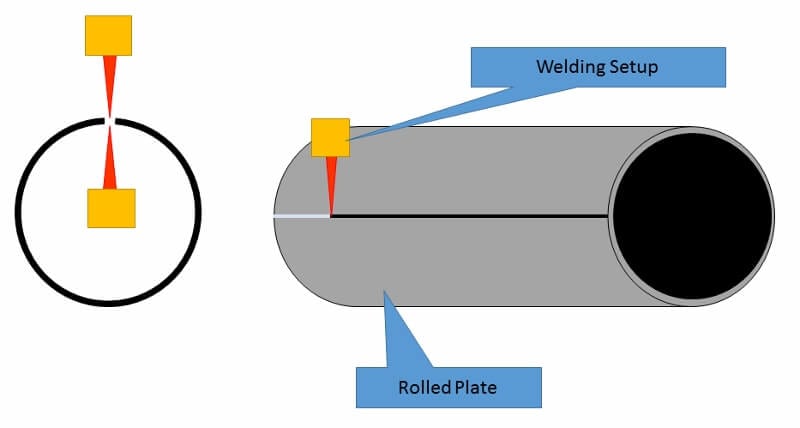
SAW Pipe Manufacturing Process
In the SAW welding process, external filler metal (wire electrodes) are used to join the formed plates. Depending on the pipe size, SAW pipes can have a single or double longitudinal seam.
SAW pipes are also available in the spiral seam, continually rolled from the single plate coil. The spiral SAW pipe’s production rate is very high compared to the Straight SAW pipe. However, Spiral SAW pipes are only used in low-pressure services such as water, non-critical process services, etc.
Are You Piping Components Master?