A pump is a mechanical product. It is made of several different parts. Based on the type of pump, it may have different parts. Here, I have covered the most commonly found centrifugal pump parts that you may find in almost all pumps.
- Body / Casing
- Impeller
- Wear Ring
- Shaft
- coupling
- Bearing and Bearing housing
- Sealing system
- Suction / Discharge Flanges
- Support frame
Here in the exploded 3D model, you can see the different parts of the pump. This is a simple pump that is used in water applications. I have marked all the components listed above.
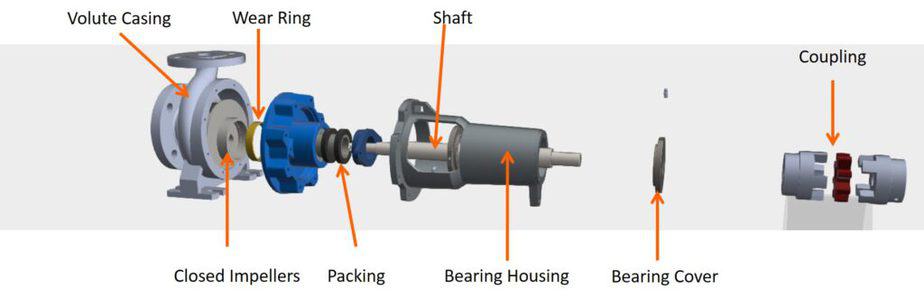
Let’s start with the first centrifugal pump part.
Body / Casing
The pump body is also known as a casing. It is the largest component of the pump. It can be fabricated or made for the casting. Most pumps that you will see in the process plant have cast bodies. Forged or fabricated casing is used for special application pumps where casting is difficult or costly.
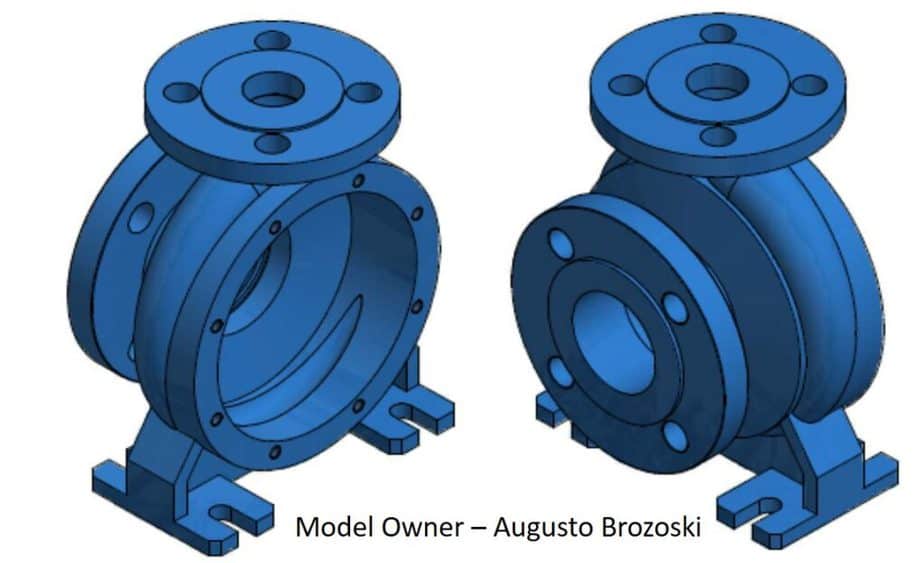
Body host all other components of the pump. It will also provide the passage for fluid. The volute design of the body helps in increasing the pressure head by converting energy.
Depending on the pressure and fluid property, it can be manufactured from different materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel.
There are different types of casing designs available to meet different pump designs.
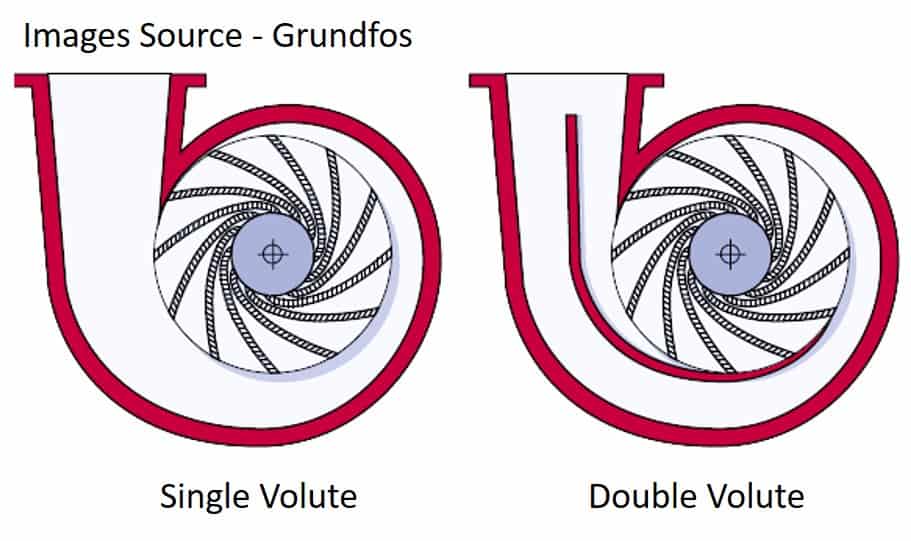
Single and Double volute body
Here in the photo, you can see the single and double volute casing design. Pump with large radial force uses a double casing body to reduce the force body.
Centrifugal Pump Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz
Single and Double suction body
Here in the photo, you can see the single and double suction casing design. In a double suction design, fluid can enter from both sides of the impeller. This is more complex than single-suction.
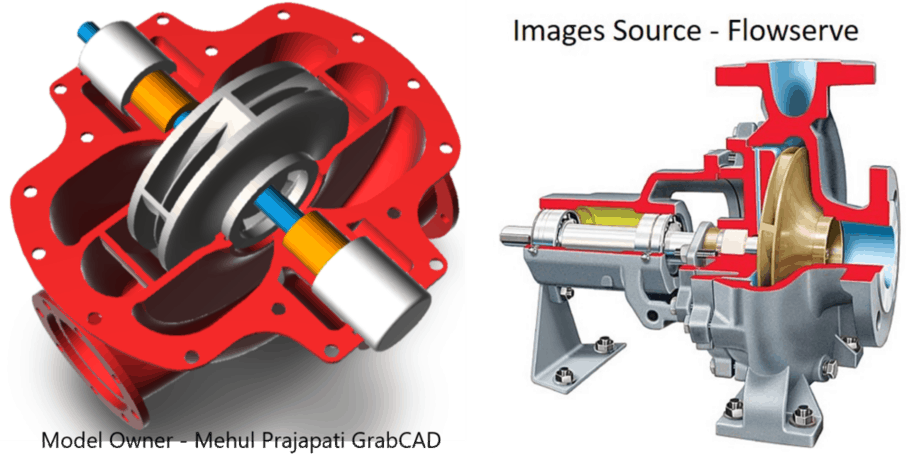
Single and Multi stage body
As you can see in the photo, a multi-stage pump body is bigger and more costly than a single-stage pump.
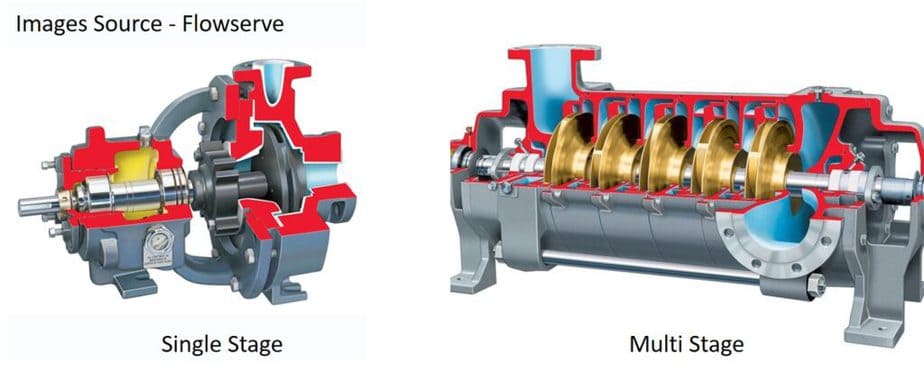
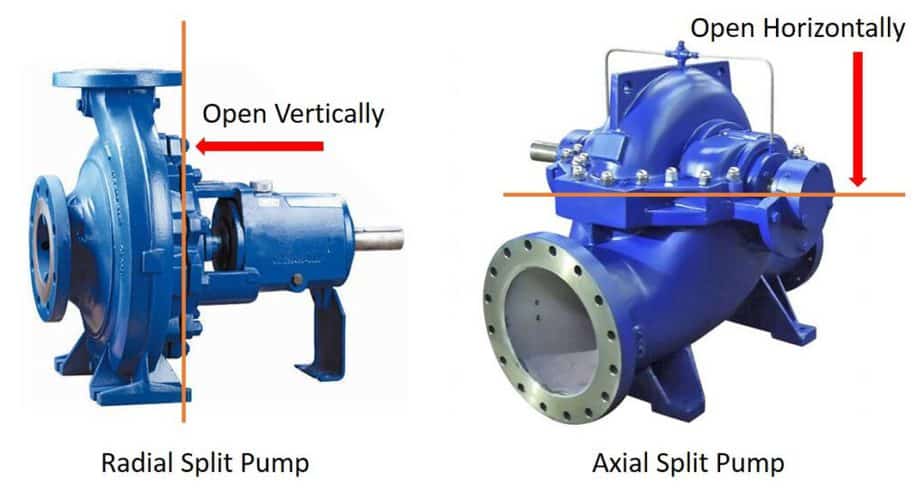
Radial and Axial Split body
Depending on the pump type, whether radial or axial, the pump body can be manufactured accordingly. In the photo here, you can see these types.
Impeller
The impeller is the most critical part of pump performance. Proper impeller design and selection will decide the efficiency of the pump. It transfers energy from the driver to fluid. It converts kinetic energy into the pressure head of the pump.
Impeller has a curved blade, which is also known as a vane, and it is mounted on the pump shaft.
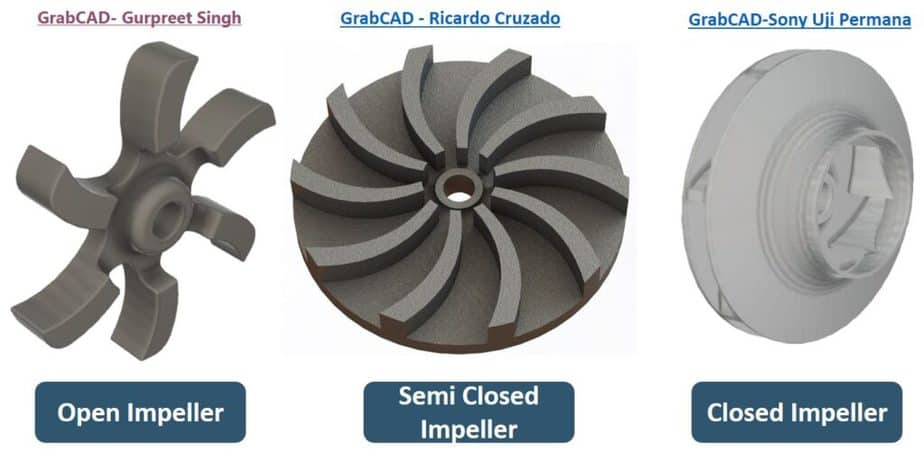

There are three basic impeller designs available. Here you can see the same in the image.
- Open Impeller
- Semi-closed Impeller
- Closed Impeller
Open Impeller
It is the most simple design. The Vane of this type of impeller is open on the side. Due to this design, it is structurally weak as compared to the other two types. The open impeller is used in the service with particles. You can also see this type of impeller in a cheap low, duty pump.
Semi-closed Impeller
In this design, one side of the impeller vanes is attached with a circular disc. This impeller is stronger than the open impeller and provides better performance. This impeller can handle liquid with some particles without choking.
Closed Impeller
Pumps used in process plants have closed impellers. In this type, vanes are enclosed from both sides. In the image, you can see this type. A closed impeller is difficult to manufacture and costly. It gives the best performance and high efficiency. It is used with clear liquid and cannot be used in liquid with suspended particles.
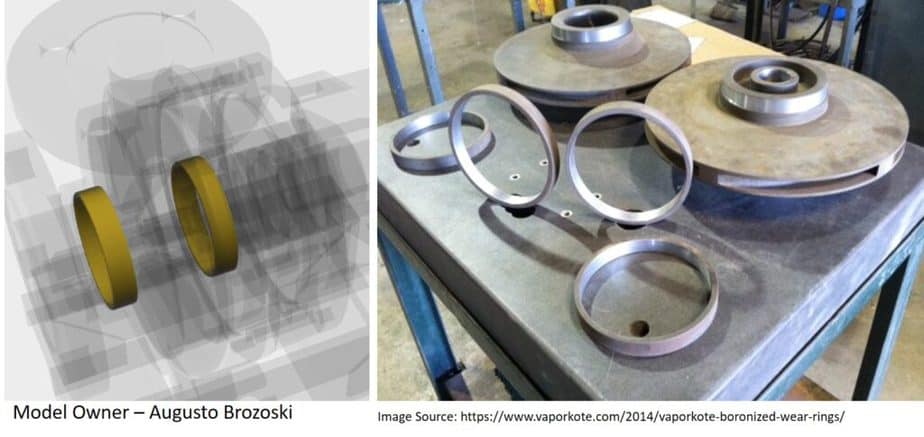
Wear Ring
You can see the wear rings used to prevent damage to the impeller and pump body in the image here. The wear ring’s function is to protect costly impeller and body from damage due to high speed. You can replace these rings at periodic maintenance.

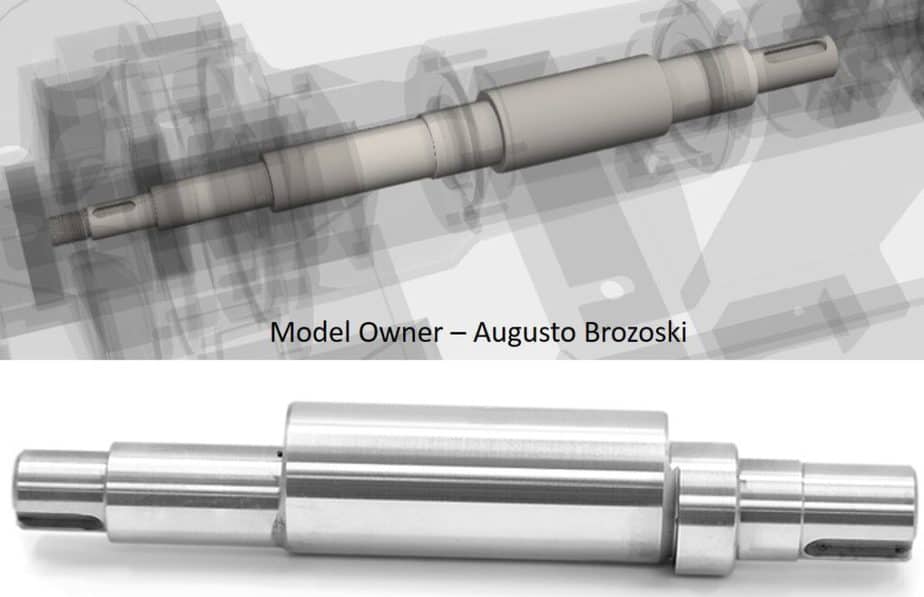
Shaft
The function of the pump shaft is to transfer the drive energy to the impeller. It is forged steel with a machined surface. Depending on pump design, it can be overhang type such as in single stage end suction pump or supported at both ends such as between bearing pump.

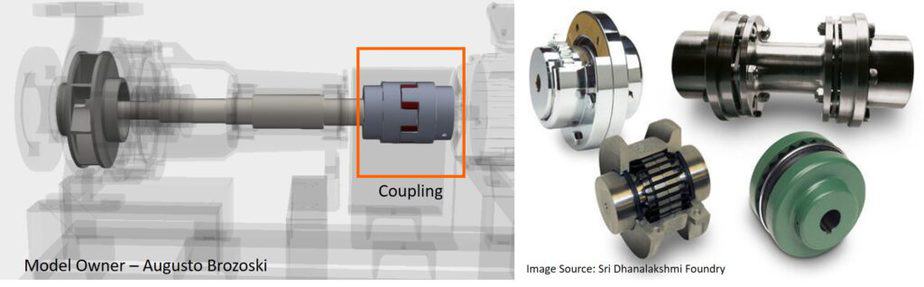
Coupling
The coupling is used to connect the pump with the driver (Motor/engine/turbine). There are two types of pump couplings used in the pump used in the process plant.
Fixed or rigid coupling: This type of coupling is used when you have a perfectly aligned driver and pump. It is not suitable for most pumps used in process plants. If there is misalignment, it will create high stress in the shaft.
Flexible coupling: This type is regularly used in a pump as this can compensate for some amount of both radial and axial misalignment.
In the image here, you can see both types of pump coupling.
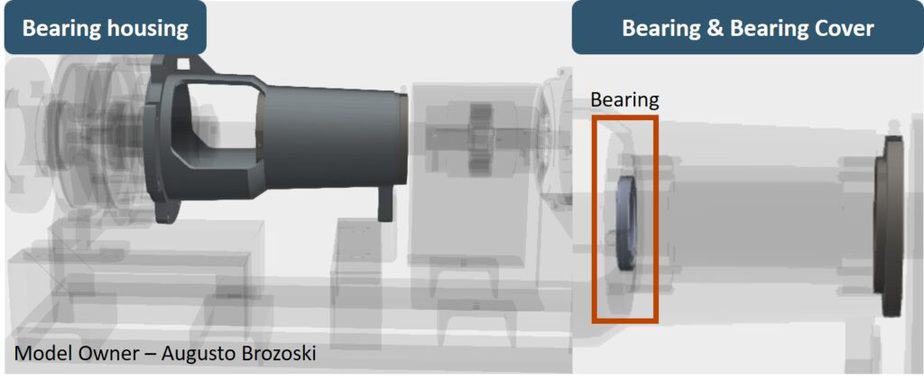
Bearing and Bearing housing
Most centrifugal pumps use standard roller bearing. The bearing’s function is to keep the shaft in position, facilitating the shaft’s frictionless movement. Bearings are one of the most critical components of the pump, as improper selection leads to the pump’s failure.
Bearing housing is the place where bearings are installed. Lubricant is filled in this hosing to keep the bearing cool and well lubricated to achieve the best performance.
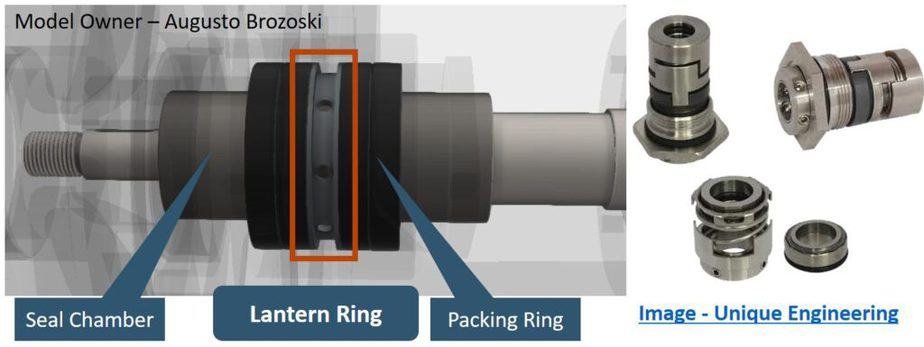
Sealing system
The function of the sealing system is to prevent the leaking of the liquid from the pump. Depending on the properties of the liquid being handled, complexity is involved. The pump sealing system can be as simple and complex at the same time.
A simple gland packing is enough for a water pump. Whereas for toxic or flammable liquid, a separate sealing system is required. Different types of mechanical seals are available to meet these requirements.
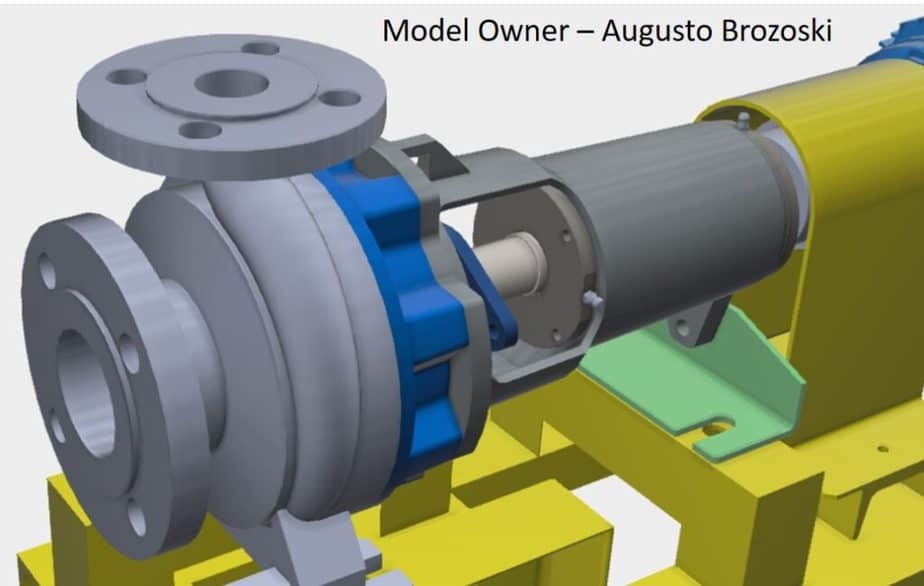
Suction / Discharge Flanges
Suction and discharge flanges are part of the pump body. It can be an end-suction top discharge or radial type. Dimensions of these flanges are machined to match connecting pipe flanges. Sometimes you can see the small ring welded inside the discharge flange to achieve the design flow rate.
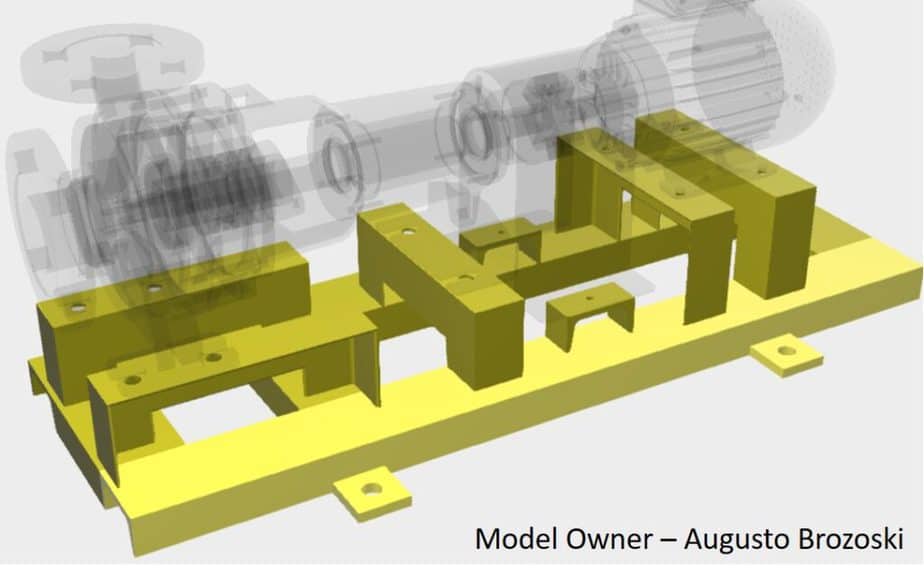
Support Frame
Pumps are mounted on the structural support frame. This frame provides the base for the pump and driver. Proper design is necessary to avoid the vibration of the pump. Some engine-driven pump drivers are installed on a separate frame.
The frame is constructed from I-Beam and Channel to provide strength. This is all about centrifugal pump parts. You can learn about different types of centrifugal pumps and API 610 pumps by checking those articles.
Are You Piping Components Master?