What is the difference between Pipe and Tube? At the end of this video, you will know the difference from an oil & gas engineer’s point of view.
You are aware that people use the term pipe and tube interchangeably. However, there is a difference between pipe and tube.
What is Pipe?
The pipe is a pressure-tight circular hollow section used in piping systems to transport gases or fluids.
What is Tube?
Over the internet, you will find that tube is a circular structural member, and the confusion starts from here. In oil and gas industries, tubes are used not just as a structural part but also in the heat exchanger and fired heater for a process application.
Let’s check the difference. The first difference is how the size is defined for the pipe and tube.
Five Differences Between Pipe and Tube
1. The difference in the way size mentioned
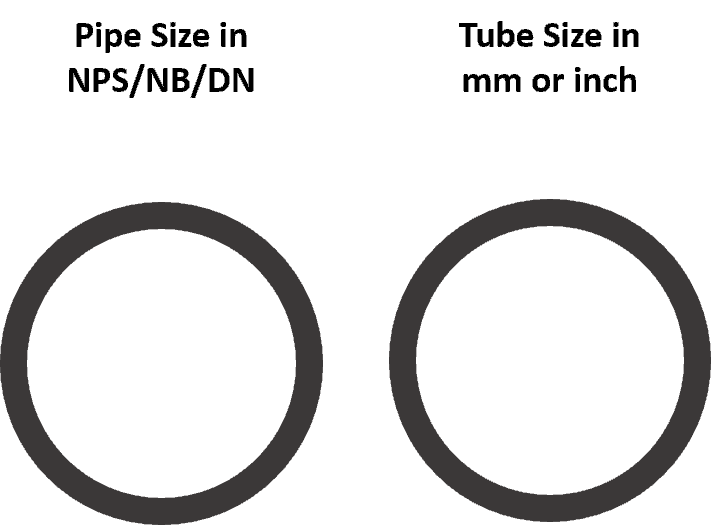
American code & Standard related to oil & gas, such as ASME B31.3 Process Piping code & ASME section IX Pressure vessel design code, use the term NPS – Nominal Pipe Size to define the diameter of the pipe.
Whereas in the case of tubes, tube size is defined in fixed numbers, either in mm or inches.
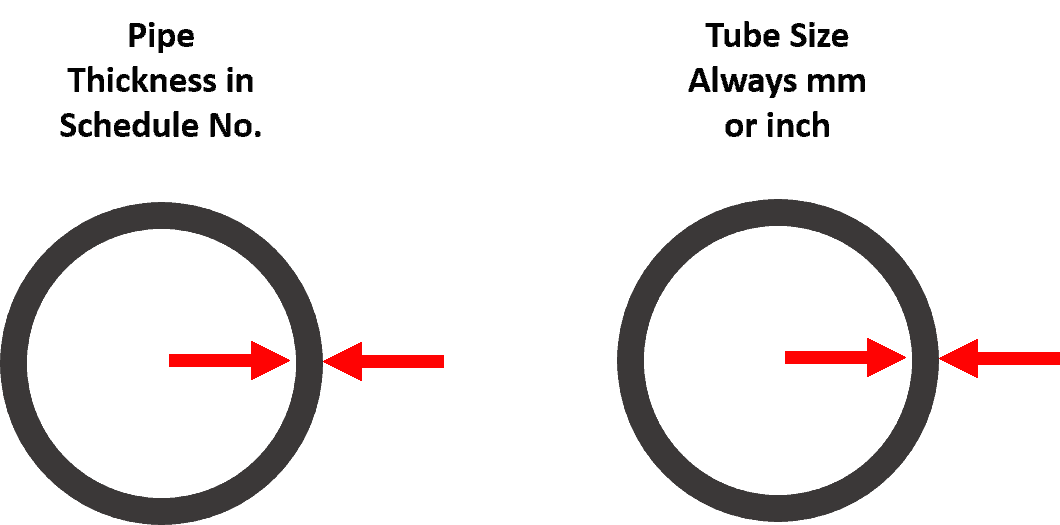
2. The difference in the way thickness mentioned
Pipe thickness is specified in a schedule number, whereas tube thickness is specified in a fixed number, either in mm or inches.
Piping Component Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
| Diffrances | Pipes | Tubes |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Pipe Size Specified in Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) or Nominal Bore (NB) or Diameter Nominal (DN) | Tubes sized are specified in millimeter or in inches by outside diameter |
| Thickness | Wall thickness is expressed in schedule number | Wall thickness is expressed in millimeter, or inches, or BWG (Birmingham wire gauge.) |
| Diameter | The outside diameter of pipe up to size 12” is numerically larger than corresponding pipe size | Outside diameter of tubes is numerically equal to the corresponding size. |
| Use | Used in all process & utility lines | Generally used in tracing lines, tubes for heat exchanger & fired heater & in instrument connection. |
| Also used as a structural member | Also used as a structural member | Also used as a structural member |
| Availability | Available in the small bore as well as the big bore. | Normally small-bore tube is used in process piping. For structural use, tubs are available in custom sizes. |
These are the only things that you have to know when you differentiate pipe and tube.
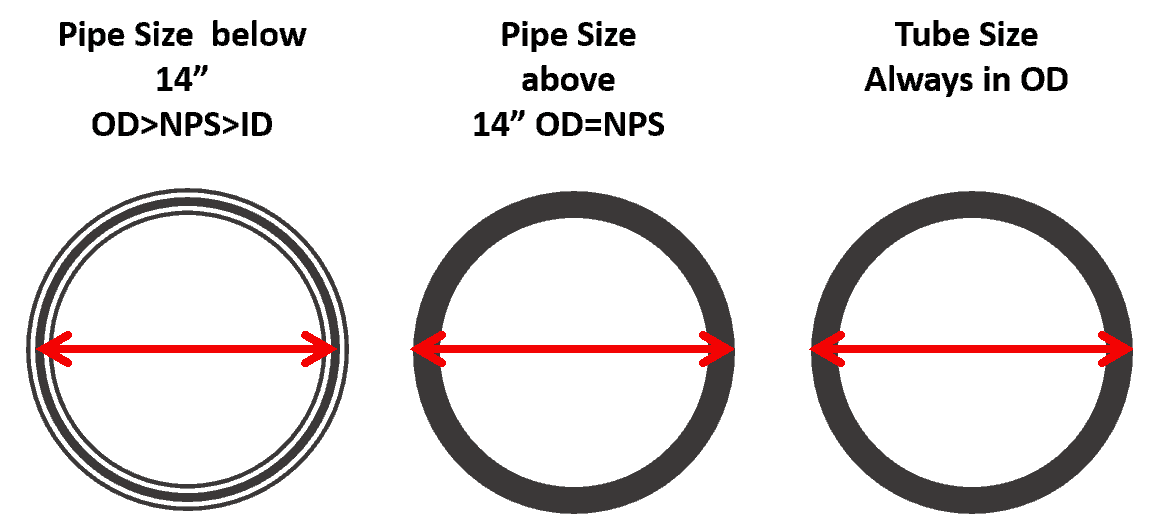
3. The difference in the way OD mentioned
A few other things you have to know are that up to 12″ NPS pipe outside diameter of the pipe is more than 12″ and above 12″, it is the same as pipe size. Whereas the tube’s outside diameter is always equal to the size of the tube.
The 2nd thing you must remember is that the outside diameter of both pipe & tube is standardized, so whenever thickness changes inside diameter will change.
4. The difference in the Use of Pipe & Tube in Oil & Gas
As said earlier, pipes are used in all kinds of process fluids and services. Tubes are generally used for heat transfer applications such as heat tracing lines, heat exchangers, and fired heaters and are also used as instrument connection lines.
Tubes are also used for civil structure applications as primary load-bearing members in steel structures.
5. Availability in the Sizes
Pipes are available in a standard size of 1/8″ to 80″, whereas tubes used in oil & gas are generally of small size. Structural tubular are available in all desired sizes.
As the difference between Pipe and Tube are sometimes confusing, similarly Piping and Pipeline are also confusing. Learn the differences between piping and pipeline by clicking on this link.
Are You Piping Components Master?