In this video, you will learn about Seamless Pipe Manufacturing processes such as Mandrel Mill Process, Mannesmann Plug Mill Process, Forging Process, and Extrusion Process that are used to manufacture seamless pipe.
Mandrel Mill Process
In Mandrel Mill Pipe Manufacturing Process, steel billet is heated to forging temperature in the rotary furnace. A cylindrical hollow, also known as a mother hollow, is produced with the help of a rotary piercer and a set of roller arrangements that keep the piercer at the center of the billet.
The outside diameter of the piercer is approximately that of the inside diameter of a finished pipe. With the help, a secondary roller arrangement known as MPM -(Multi Stand Pipe Mill) outside diameter and thickness are achieved.
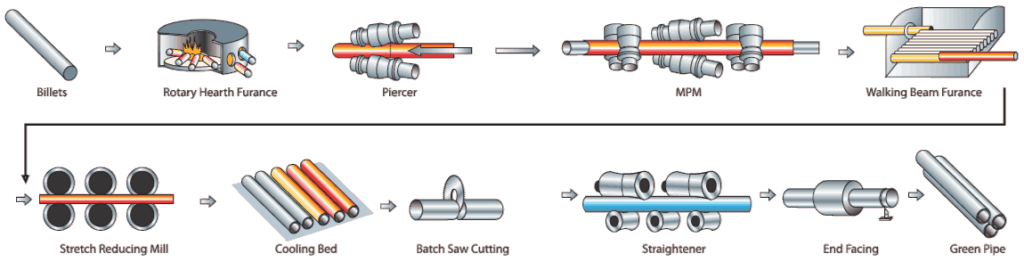
To maintain temperature, the pipe is sent to the reheating furnace, which increases the temperature of the pipe. In the next stage, the pipe is sent to the scratch-reducing mill that improves the dimension and surface finish of the pipe.
After that pipe, the temperature is reduced to atmospheric temperature on the cooling bed. These cooled pipes are then cut to size and sent for straightening. These finished pipes are then sent for various NDT inspections, such as eddy current and ultrasonic inspection.
Once NDT is cleared, pipes are hydro-tested to ensure strength and ability to remain leak-proof under pressure. In the last stage of inspection, a competent inspection engineer visually and dimensionally checks the pipes.
He will ensure that the pipe is meeting the code, standard, and specification requirements. Once the Inspection engineer cleared the pipe, it will mark as per standard requirements & send for packaging.
Mannesmann Plug Mill Process
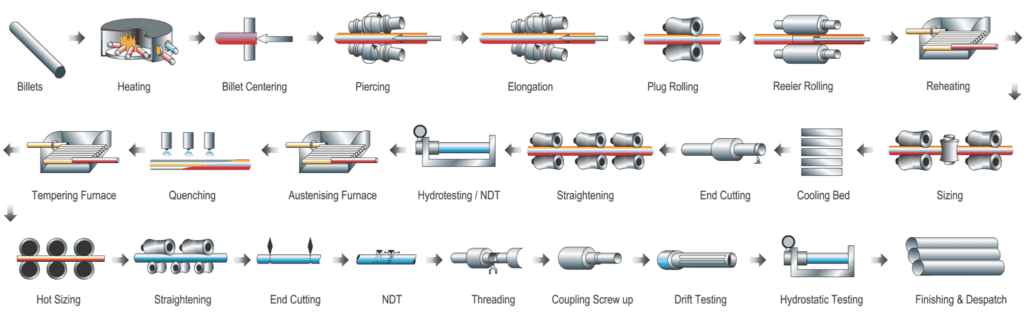
Mannesmann was a German engineer who invented this method. The difference between the Plug mill process and the Mandrel mill process is that in the mandrel method, inside diameter is achieved in a single pass, whereas in Mannesmann, a multi-stage reduction is possible.
So you have greater thickness reduction as compared to the Mandrel process. Here in this process chart, you can see the heat treatment furnace after the hydro test.
Stainless steel, low alloy steel, and higher thickness carbon steel pipes are subjected to various heat treatments such as Normalizing, Quenching, Tempering, Solution Annealing, Stress relieving, or it is a combination of these treatments. As explained earlier, a finished pipe is passed through various quality testing before it can be certified for use.
Piping Component Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
Forging Process to Manufactured Seamless Pipes
In a Forging process, a heated billet is placed in a forging die that has a diameter slightly larger than a finished pipe. A hydraulic press of forging hammer with matching inside diameter is used to create cylindrical forging. Once this forging is done pipe is machined to achieve the final dimension. Forging is used to manufacture large diameter seamless pipes that cannot be manufactured using traditional methods. Forged pipes are normally used for steam header and pressure vessel shells.
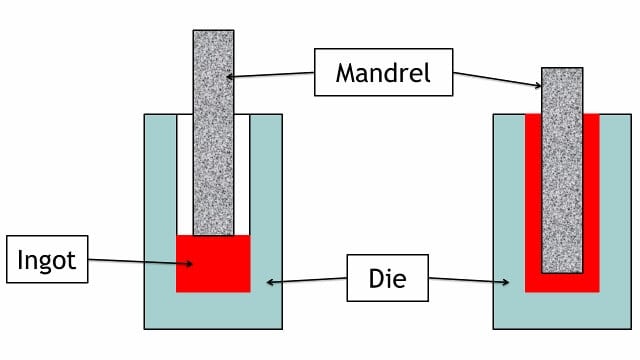
Extrusion Method for Seamless Pipe Manufacturing
In an extrusion method, a heated billet is placed inside the die. A hydraulic ram pushes the billet against the piercing mandrel, material flows from the cylindrical cavity between die and mandrel. This action produces the pipe from the billet. Sometimes, manufactured produce pipe with a high thickness known as mother hollow. Many secondary pipes manufactured used this mother hollow to produce pipes with different dimensions with the help of the extrusion process.
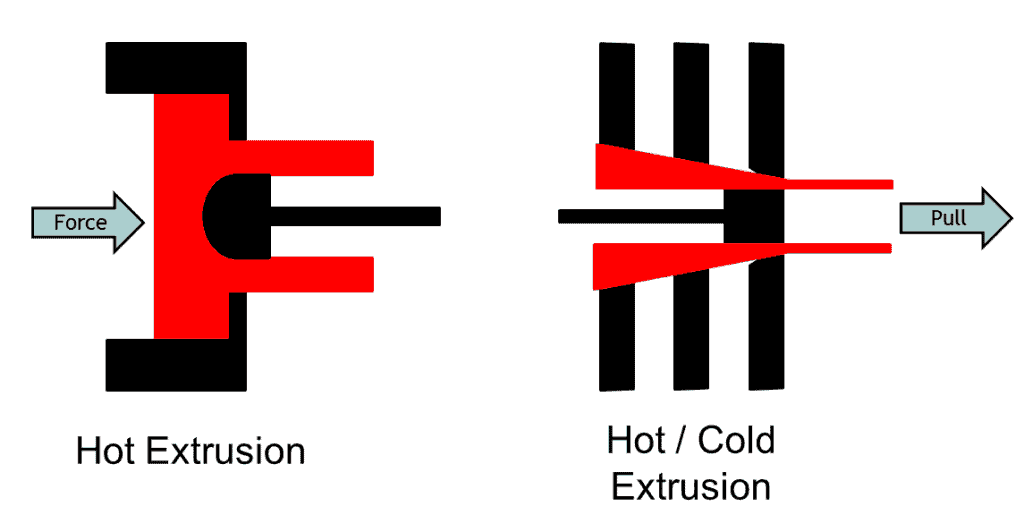
This is all about the seamless pipe manufacturing process. Please do check another video to learn about the welded pipe manufacturing process.
Subscribe to my YouTube Channel – https://goo.gl/LSMDCV
Are You Piping Components Master?