Flange joints require proper tightening to avoid the leak of fluid from the joint. The bolt tightening sequence or torque sequence is defined in the torque tightening procedure. Most companies have their Flange bolt torque tightening procedure used during the plant’s construction and operation.
Flange joints are torque tight with the help of a torque wrench (Manual or hydronic wrench). The clamp load produced during tightening is higher than 75% of the fastener’s proof load. To achieve the benefits of the pre-loading, the clamping force in the screw must be higher than the joint separation load.
When the bolt loading requires a torque higher than 678 Nm (500 ft-lbs.) to be applied, hydraulic bolt torquing is recommended.
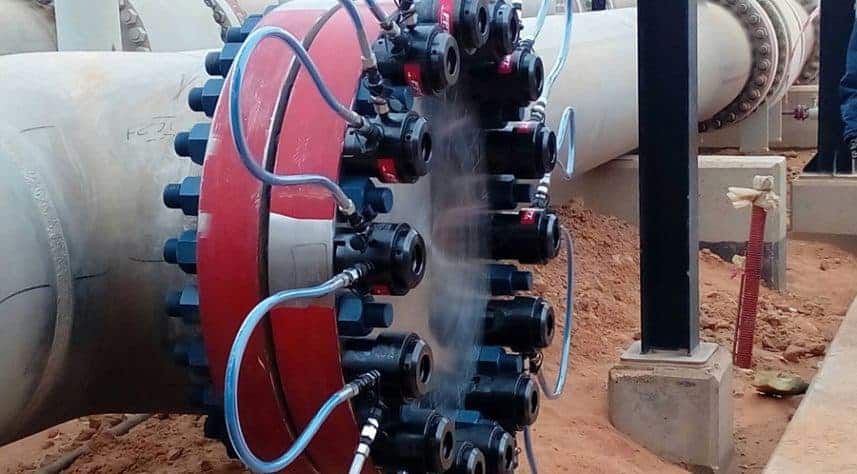

Image source- Fluid Power Technology
The torque value is dependent on the friction between the stud bolt threads and the nut head, this friction can be affected by applying a lubricant, or any plating (e.g., Cadmium or Zinc) applied to the stud threads. The bolting standard will define whether the torque value is for a dry or lubricated stud/bolt thread. If a bolt is torqued rather than the nut, then the torque value should be increased to compensate for the additional friction – bolt should only be torqued if they are fitted in clearance holes.
The bolts shall be tightened by torque control, using the Anti-seize lubricant shall be used such as Molykote or equivalent, before installation. The specified method of bolt tightening is equally applicable to coated, galvanized, and ungalvanized bolts.
Flange stud Torque Sequence is extremely important to properly tighten the flange joint. In this detailed article, I have tried to simplify this Torque Sequence so that you achieve the desired result without damaging the flange and studs.
Pre-checks for Bolt Tightening
Flange Condition
- Check conditions of flange faces for scratches, dirt, and scale.
- Check for corrosion pitting and tool marks.
- Inspect the gasket seating surfaces.
- Check the areas on the flange where the nuts will sit, it should be flat and free from pitting and excessive wear.
- RTJ Grooves must be kept clean, corrosion-free & undamaged.
The acceptable imperfection of the Pipe flange raised face is given in ASME 16.5 table 3. Refer to the table for Permissible Imperfections in Flange Facing Finish for Raised Face Flange.
| Size in Inch | Size in mm | Maximum Radial Projection of Imperfections that are | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Deeper Than the Bottom of the Serrations, mm | Deeper Than the Bottom of the Serrations, mm | ||
| 1/2 | 15 | 3.0 | 1.5 |
| 3/4 | 20 | 3.0 | 1.5 |
| 1 | 25 | 3.0 | 1.5 |
| 1 1/4 | 32 | 3.0 | 1.5 |
| 1 1/2 | 40 | 3.0 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 50 | 3.0 | 1.5 |
| 2 1/2 | 65 | 3.0 | 1.5 |
| 3 | 80 | 4.5 | 1.5 |
| 3 1/2 | 90 | 6.0 | 3.0 |
| 4 | 100 | 6.0 | 3.0 |
| 5 | 125 | 6.0 | 3.0 |
| 6 | 150 | 6.0 | 3.0 |
| 8 | 200 | 8.0 | 4.5 |
| 10 | 250 | 8.0 | 4.5 |
| 12 | 300 | 8.0 | 4.5 |
| 14 | 350 | 8.0 | 4.5 |
| 16 | 400 | 10.0 | 4.5 |
| 18 | 450 | 12.0 | 6.0 |
| 20 | 500 | 12.0 | 6.0 |
| 24 | 600 | 12.0 | 6.0 |
Flange and Olet Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
Flange Alignment Checks.
Visually examine the flange alignment to ensure that an acceptable fit has been obtained. While aligning flanges, make sure that there are no residual stresses in the joint. Using heat correction for flange alignment is not a good practice and should be strictly prohibited.
- Flange faces should be parallel and aligned.
- The flange bolt holes should be in line so that the bolts will pass freely.
Nut, Stud or Bolt Checks
- Visually examine nuts & Stud/bolts before installation to assure they are free from defects such as corrosion, damaged threads, etc. Nut-bolts with damaged threads should not be used.
- Check the length of the stud or bolt to avoid short bolting and excessive threads. Flange bolts shall be furnished with insufficient length to allow the use of bolt tensioning equipment or spades, spacers, drip rings, and wafer valves, and the associated extra gaskets.
- Visually examine studs and nuts after cleaning to ensure they are free from burrs. Studs and nuts shall be cleaned using a wire brush to remove any dirt on the threads. Lubricant (MOLYKOTE) shall be applied on threads and nuts to flange contact surfaces. Lubricant shall not be used in the gasket and the gasket seating area.
- The bolt and nut material grades should be correctly identified before they are used.
- Bolts and nuts can only be reused if it is known that they have not been overloaded or exceeded their yield point.
- The nut identification marking must always point outwards when assembling the nut on the bolt.
Gasket Checking
- Do not use sealing compound, grease, or other paste or adhesive on gasket or flange faces.
- While gasket insertion, it shall not be forced into the gasket seat between the mating flange faces. Once the gasket is seated, the mating flanges are brought together carefully without shaking the gasket off the seat, installing all studs, and running up all nuts hand tight.
- Visually examine gaskets before installation to assure they are free from defects.
- Color coding shall be maintained as per the rate and type of gasket provided by the manufacturer.
- Clean gasket seating face using a wire brush.
- Make sure the material is as specified; look for any possible defects or damage in the gasket, such as folds or creases.
- All Soft material gaskets should be replaced with new ones whenever an opened joint is to be closed again.
- The spiral wound gasket shall be used only once.
Flange Bolt Torque Sequence
Once all pre-checks are completed. You can go ahead with tightening the stud in the pre-defined torque sequence mentioned here. Torque bolts and nuts in a “CRISS-CROSS” sequence using a minimum of three torquing passes and the maximum bolt stress as defined.
- PASS 1 Torque Sequence: Torque to a maximum of 30% of the final torque value in accordance with the torque sequence. Check that gasket is getting compressed uniformly.
- PASS 2 Torque Sequence: Torque to a maximum of 60% of the final torque value.
- PASS 3 Torque Sequence: Torque to the final torque value (100%).
After the three basic torque passes are completed, repeat torquing the nuts at least once using the final torque in a “CRISS-CROSS” manner until no further rotation of the nut is observed.
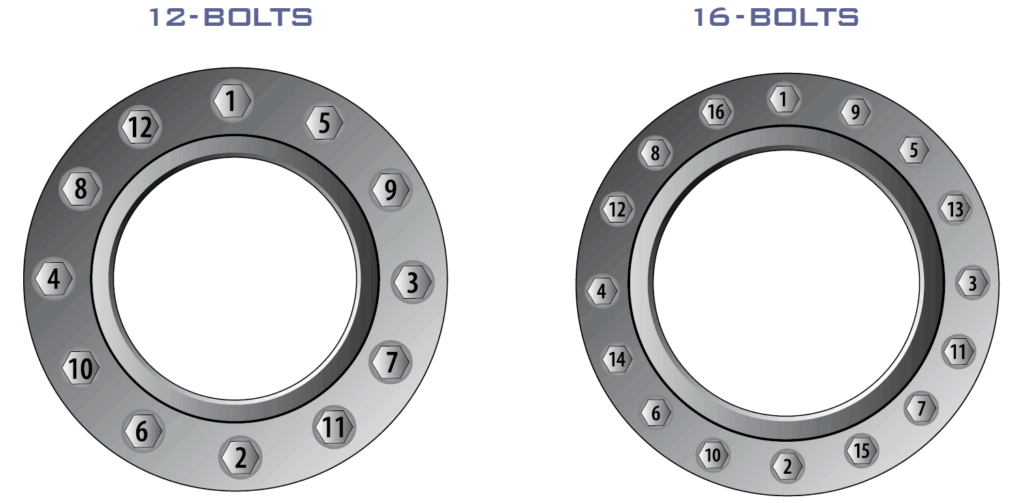
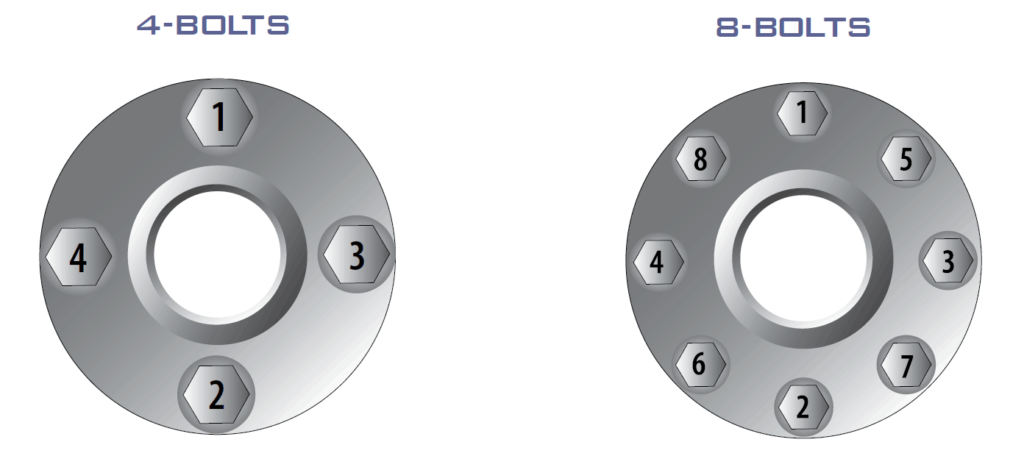
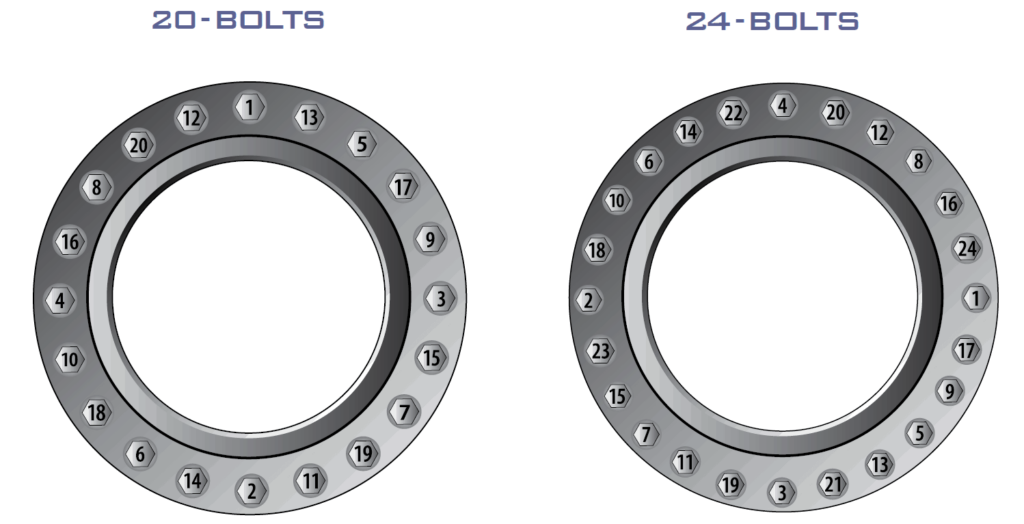
For easy handling, bolt numbering shall be done clockwise around the flange with the following sequence.
The table below shows the torque sequence for flanges with 4 to 32 bolts.
| Number of Bolt / Stud | Bolt Tightening Sequence to Follow |
|---|---|
| 4 bolt Flange | 1,3,2,4 |
| 8 bolt Flange | 1,5,3,7,2,6,4,8 |
| 12 bolt Flange | 1,7,4,10,2,8,5,11,3,9,6,12 |
| 16 bolt Flange | 1,9,5,13,3,11,7,15,2,10,6,14,4,12,8,16 |
| 20 bolt Flange | 1,11,6,16,3,13,8,18,5,15,10,20,2,12,7,17,4,14,9,19 |
| 24 bolt Flange | 1,13,7,19,4,16,10,22,2,14,8,20,5,17,11,23,6,18,12,24,3,15,9,21 |
| 28 bolt Flange | 1,15,8,22,4,18,11,25,6,20,13,27,2,16,9,23,5,19,12,26,3,17,10,24,7,21,14,28 |
| 32 bolt Flange | 1,17,9,25,5,21,13,29,3,19,11,27,7,23,15,31,2,18,10,26,6,22,14,30,8,24,16,32,4,20,12,28 |
Torque Table for Class 150 Flange
| Flange Materials : ASTM A105, ASTM A182 grades F50 and F51, ASTM A350 grades LF2 and LF3, ASTM A694 grade F52 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bolting Materials : ASTM A193 grades B7 and B7M, ASTM A320 grades L7, L7M and L43. | |||||||
| Gasket Type : Graphite Tanged Gasket | |||||||
| Bolt Lubricant Molykote 1000 (µ = 0.11) | |||||||
| Size in Inch | Size in mm | No. of Bolt | Bolt Dia. | Thread Type | Bolt Stress lb/in2 | Torque lbf.ft. | Torque Nm |
| 1/2 | 15 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 25,000 | 22 | 30 |
| 3/4 | 20 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 30,000 | 26 | 36 |
| 1 | 35 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 33,000 | 29 | 39 |
| 1 ½ | 40 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 50,000 | 44 | 60 |
| 2 | 50 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 86 | 117 |
| 3 | 80 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 86 | 117 |
| 4 | 100 | 8 | 5/8” | UNC | 40,000 | 69 | 93 |
| 6 | 150 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 45,000 | 137 | 185 |
| 8 | 200 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 45,000 | 137 | 185 |
| 10 | 250 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 40,000 | 194 | 263 |
| 12 | 300 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 40,000 | 194 | 263 |
| 14 | 350 | 12 | 1” | UN8 | 41,000 | 296 | 401 |
| 16 | 400 | 16 | 1” | UN8 | 40,000 | 289 | 392 |
| 18 | 450 | 16 | 1 1/8” | UN8 | 40,000 | 421 | 571 |
| 20 | 500 | 20 | 1 1/8” | UN8 | 40,000 | 421 | 571 |
| 24 | 600 | 20 | 1 ¼” | UN8 | 40,000 | 588 | 797 |
Torque Table for Class 300 Flange
| Flange Materials : ASTM A105, ASTM A182 grades F50 and F51, ASTM A350 grades LF2 and LF3, ASTM A694 grade F52 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bolting Materials : ASTM A193 grades B7 and B7M, ASTM A320 grades L7, L7M and L43. | |||||||
| Gasket Type : Spiral Wound and Ring Joint | |||||||
| Bolt Lubricant Molykote 1000 (µ = 0.11) | |||||||
| Size in Inch | Size in mm | No. of Bolt | Bolt Dia. | Thread Type | Bolt Stress lb/in2 | Torque lbf.ft. | Torque Nm |
| 1/2 | 15 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 40,000 | 35 | 47 |
| 3/4 | 20 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 40,000 | 69 | 93 |
| 1 | 35 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 40,000 | 69 | 93 |
| 1 ½ | 40 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 31,000 | 94 | 128 |
| 2 | 50 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 37,000 | 64 | 87 |
| 3 | 80 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 42,000 | 127 | 173 |
| 4 | 100 | 8 | 5/8” | UNC | 45,000 | 137 | 185 |
| 6 | 150 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 45,000 | 137 | 185 |
| 8 | 200 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 45,000 | 218 | 296 |
| 10 | 250 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 45,000 | 325 | 441 |
| 12 | 300 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 43,000 | 453 | 614 |
| 14 | 350 | 12 | 1” | UN8 | 45,000 | 474 | 643 |
| 16 | 400 | 16 | 1” | UN8 | 31,000 | 456 | 618 |
| 18 | 450 | 16 | 1 1/8” | UN8 | 34,000 | 500 | 678 |
| 20 | 500 | 20 | 1 1/8” | UN8 | 40,000 | 588 | 797 |
| 24 | 600 | 20 | 1 ¼” | UN8 | 31,000 | 809 | 1097 |
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
Torque Table for Class 600 Flange
| Flange Materials : ASTM A105, ASTM A182 grades F50 and F51, ASTM A350 grades LF2 and LF3, ASTM A694 grades F52 and F60 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bolting Materials : ASTM A193 grades B7 and B7M, ASTM A320 grades L7, L7M and L43. | |||||||
| Gasket Type : Spiral Wound and Ring Joint | |||||||
| Bolt Lubricant Molykote 1000 (µ = 0.11) | |||||||
| Size in Inch | Size in mm | No. of Bolt | Bolt Dia. | Thread Type | Bolt Stress lb/in2 | Torque lbf.ft. | Torque Nm |
| 1/2 | 15 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 40,000 | 35 | 48 |
| 3/4 | 20 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 40,000 | 69 | 94 |
| 1 | 35 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 40,000 | 69 | 94 |
| 1 ½ | 40 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 45,000 | 137 | 185 |
| 2 | 50 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 86 | 117 |
| 3 | 80 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 45,000 | 137 | 185 |
| 4 | 100 | 8 | 5/8” | UNC | 45,000 | 218 | 296 |
| 6 | 150 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 45,000 | 325 | 441 |
| 8 | 200 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 50,000 | 526 | 714 |
| 10 | 250 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 45,000 | 662 | 897 |
| 12 | 300 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 45,000 | 662 | 897 |
| 14 | 350 | 12 | 1” | UN8 | 45,000 | 894 | 1213 |
| 16 | 400 | 16 | 1” | UN8 | 45,000 | 1175 | 1593 |
| 18 | 450 | 16 | 1 1/8” | UN8 | 45,000 | 1507 | 2044 |
| 20 | 500 | 20 | 1 1/8” | UN8 | 45,000 | 1507 | 2044 |
| 24 | 600 | 20 | 1 ¼” | UN8 | 45,000 | 2354 | 3191 |
Torque Table for Class 900 Flange
| Flange Materials : ASTM A105, ASTM A182 grades F50 and F51, ASTM A350 grades LF2 and LF3, ASTM A694 grades F52, F60 and F65 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bolting Materials : ASTM A193 grades B7 and B7M, ASTM A320 grades L7, L7M and L43. | |||||||
| Gasket Type : Spiral Wound and Ring Joint | |||||||
| Bolt Lubricant Molykote 1000 (µ = 0.11) | |||||||
| Size in Inch | Size in mm | No. of Bolt | Bolt Dia. | Thread Type | Bolt Stress lb/in2 | Torque lbf.ft. | Torque Nm |
| 1/2 | 15 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 40,000 | 121 | 165 |
| 3/4 | 20 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 40,000 | 121 | 165 |
| 1 | 35 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 40,000 | 194 | 263 |
| 1 ½ | 40 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 45,000 | 325 | 441 |
| 2 | 50 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 40,000 | 194 | 263 |
| 3 | 80 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 243 | 329 |
| 4 | 100 | 8 | 5/8” | UNC | 45,000 | 474 | 642 |
| 6 | 150 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 50,000 | 526 | 714 |
| 8 | 200 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 45,000 | 894 | 1213 |
| 10 | 250 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 994 | 1347 |
| 12 | 300 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 994 | 1347 |
| 14 | 350 | 12 | 1” | UN8 | 50,000 | 1306 | 1770 |
| 16 | 400 | 16 | 1” | UN8 | 50,000 | 1675 | 2271 |
| 18 | 450 | 16 | 1 1/8” | UN8 | 50,000 | 2615 | 3545 |
| 20 | 500 | 20 | 1 1/8” | UN8 | 50,000 | 3195 | 4332 |
| 24 | 600 | 20 | 1 ¼” | UN8 | 45,000 | 5713 | 7746 |
Torque Table for Class 1500 Flange
| Flange Materials : ASTM A105, ASTM A182 grades F50 and F51, ASTM A350 grades LF2 and LF3, ASTM A694 grades F52, F60 and F65 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bolting Materials : ASTM A193 grades B7 and B7M, ASTM A320 grades L7, L7M and L43. | |||||||
| Gasket Type : Spiral Wound and Ring Joint | |||||||
| Bolt Lubricant Molykote 1000 (µ = 0.11) | |||||||
| Size in Inch | Size in mm | No. of Bolt | Bolt Dia. | Thread Type | Bolt Stress lb/in2 | Torque lbf.ft. | Torque Nm |
| 1/2 | 15 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 40,000 | 121 | 165 |
| 3/4 | 20 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 45,000 | 137 | 185 |
| 1 | 35 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 45,000 | 218 | 296 |
| 1 ½ | 40 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 50,000 | 361 | 489 |
| 2 | 50 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 243 | 329 |
| 3 | 80 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 526 | 714 |
| 4 | 100 | 8 | 5/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 735 | 997 |
| 6 | 150 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 50,000 | 994 | 1347 |
| 8 | 200 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 50,000 | 1675 | 2271 |
| 10 | 250 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 2615 | 3545 |
| 12 | 300 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 3193 | 4329 |
| 14 | 350 | 12 | 1” | UN8 | 45,000 | 4133 | 5603 |
| 16 | 400 | 16 | 1” | UN8 | 45,000 | 5713 | 7746 |
| 18 | 450 | 16 | 1 1/8” | UN8 | 45,000 | 7652 | 10375 |
| 20 | 500 | 20 | 1 1/8” | UN8 | 45,000 | 9986 | 13539 |
| 24 | 600 | 20 | 1 ¼” | UN8 | 45,000 | 15983 | 21670 |
Torque Table for Class 2500 Flange
| Flange Materials : ASTM A105, ASTM A182 grades F50 and F51, ASTM A350 grades LF2 and LF3, ASTM A694 grades F52, F60 and F65 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bolting Materials : ASTM A193 grades B7 and B7M, ASTM A320 grades L7, L7M and L43. | |||||||
| Gasket Type : Spiral Wound and Ring Joint | |||||||
| Bolt Lubricant Molykote 1000 (µ = 0.11) | |||||||
| Size in Inch | Size in mm | No. of Bolt | Bolt Dia. | Thread Type | Bolt Stress lb/in2 | Torque lbf.ft. | Torque Nm |
| 1/2 | 15 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 45,000 | 137 | 185 |
| 3/4 | 20 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 50,000 | 152 | 206 |
| 1 | 35 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 50,000 | 243 | 329 |
| 1 ½ | 40 | 4 | ½” | UNC | 55,000 | 579 | 785 |
| 2 | 50 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 55,000 | 397 | 538 |
| 3 | 80 | 4 | 5/8” | UNC | 55,000 | 809 | 1097 |
| 4 | 100 | 8 | 5/8” | UNC | 55,000 | 1436 | 1947 |
| 6 | 150 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 50,000 | 3195 | 4332 |
| 8 | 200 | 8 | ¾” | UNC | 50,000 | 3195 | 4332 |
| 10 | 250 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 6348 | 8606 |
| 12 | 300 | 12 | 7/8” | UNC | 50,000 | 8502 | 11527 |
Disclaimer – Please check with Professional Engineer before using it.
Are You Piping Components Master?