In this article, I will explain about PSL1 Vs PSL2 API 5L Linepipe. Many people find it difficult to identify differences between PSL1 And PSL2 Pipes. (PSL1 Vs. PSL2 Pipes)
Please subscribe to my channel to get regular updates on the new video. If you like this video, please share this video with your friends and help me to grow my channel.
An API 5L line pipe is manufactured in two varieties, PSL 1 and PSL 2. But what is PSL? PSL stands for Product Specification Levels. PSL stands for Product Specification Levels.
Pipes are used in different types of environments, such as corrosive and non-corrosive. Pipes used in severely corrosive environments require material that can withstand such process conditions. On the other hand, a standard quality level pipe for normal services will also serve the purpose.
Differences between PSL1 and PSL2 pipes are as follows;
- Chemical Properties
- Mechanical Properties
- Manufacturing Methods
- Inspection and Defect Repair
- Certification & Traceability
Chemical Properties
| PARAMETER | PSL1 | PSL2 |
|---|---|---|
| Chemistry: Max C for Seamless pipe | 0.28% for grades ≥ B | 0.0024 |
| Chemistry: Max C for Welded pipe | 0.26% for grades ≥ B | 0.0022 |
| Chemistry: Max P | 0.03% for grades ≥ A | 0.0003 |
| Chemistry: Max S | 0.0003 | 0.0002 |
| Carbon equivalent: | Only when purchaser specifies SR18 | Maximum required for each grade |
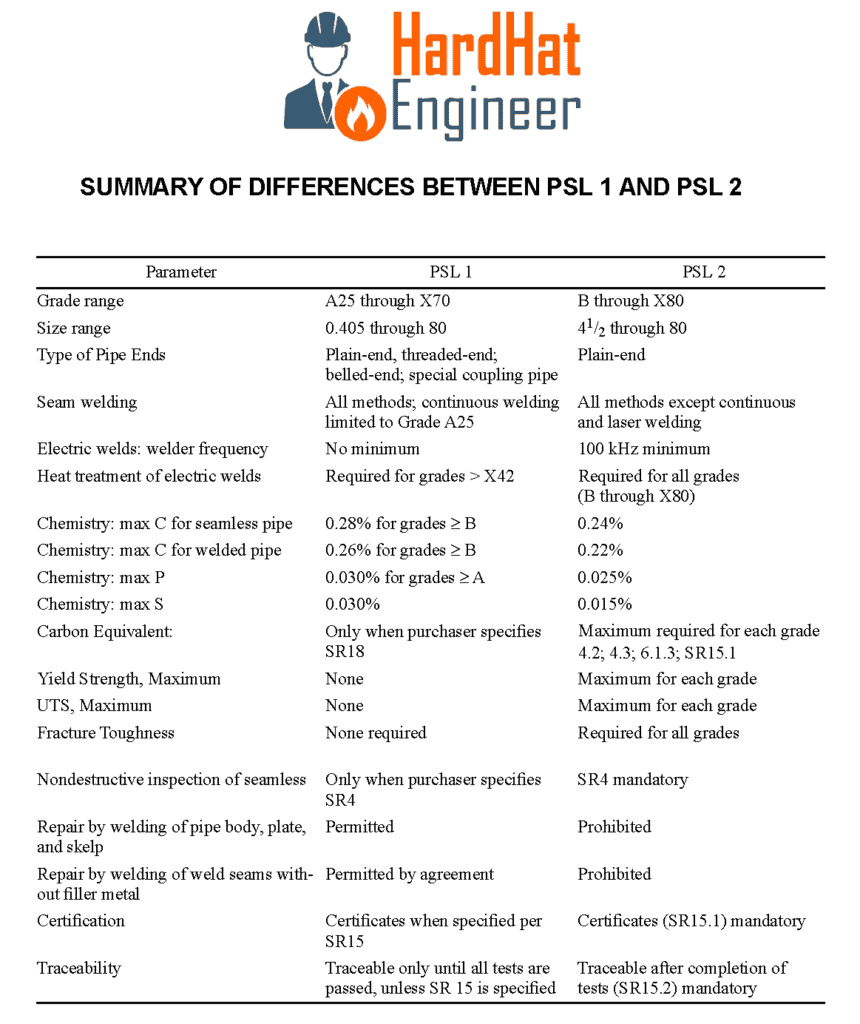
Three elements change when requirements change from PSL1 to PSL2.
The first is Carbon.
Maximum Carbon for Seamless PSL1 pipe is 0.28% for grade B & higher. For all grades of PSL2 pipes, the maximum carbon is 0.24%.
Similarly, for welded PSL1 pipe, Maximum Carbon is 0.26% for grade B & higher. For all grades of PSL2 welded pipes, the maximum carbon is 0.22%.
The second element is Phosphorus.
For PSL1 pipe, Maximum Phosphorus is 0.03% for grade A & higher. For all grades of PSL2 pipes, the maximum Phosphorus is 0.03%. So, the only difference is a grade lower than A.
The third element is Sulphur.
For PSL1 pipe, the Maximum Sulphur is 0.03%. For PSL2 pipes maximum Sulphur is 0.02%.
Other than these three elements, for PSL2 pipe meeting, the Carbon equivalent is mandatory, whereas, for PSL1 pipe, it is only required if the purchaser has specified SR18. SR18 means Supplementary Requirement No.18.
Piping Component Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz
Mechanical Properties
| PARAMETER | PSL1 | PSL2 |
|---|---|---|
| Yield strength, maximum | None | Maximum for each grade |
| UTS (Ultimate Tensile Strength) maximum | None | Maximum for each grade |
| Fracture toughness | None required | Required for all grades |
For PSL2 pipe, there is a limit on Maximum Yield & Ultimate Tensile Strength, whereas for PSL1 pipe, meeting the minimum requirements is sufficient. The second requirement that is mandatory for the PSL2 pipe is Fracture toughness which is not required for the PSL1 pipe.
The difference between PSL1 & PSL2 Pipes Manufacturing
| PARAMETER | PSL1 | PSL2 |
|---|---|---|
| Grade Range | A25 through X70 | B through X80 |
| Size range | 0.405″ through 80″ | 4.5″ through 80″ |
| Type of ends | Plain end, Threaded end,Bevelled end special coupling pipes | Plain end |
| Seam welding | All methods: continuous welding limited to A25 | All methods: except continuous welding and laser welding |
| Electric welds: welder frequency | No minimum | kHz minimum 100 |
| Heat treatment of electric welds | Required for grades >X42 | Required for all grades (B through X80) |
Here in this table, you can see the differences between PSL1 & PSL2 Pipes Manufacturing. PLS1 pipes are available in grades A25 through X70, whereas PSL2 pipes are available in Grade B through X80.
PSL1 pipes are available in sizes 0.405” to 80”, whereas the smallest diameter pipe available in PSL2 is 4.5” and the largest diameter is 80”.
PSL1 pipes are available in different types of ends, such as Plain end, Threaded end, Bevelled end, and special coupling pipes, whereas PSL2 pipes are available only in Plain End.
All kinds of welding methods are acceptable to manufacture PSL1; however, continuous welding is limited to Garde A25. For PSL2 welded pipes, except continuous welding and laser welding, all other welding methods are acceptable.
For electric weld welder frequency for PSL2 pipe is a minimum 100kHz, whereas there is no such limitation on the PLS1 pipe. Heat treatment of electric welds is required for all Grades of PSL2 pipes, whereas for PSL1 pipes, it is required for grades higher than X42.
Inspection and Defect Repair
| PARAMETER | PSL1 | PSL2 |
|---|---|---|
| Non-destructive inspection of Seamless | Only when purchaser specifies SR4 | SR4 mandatory |
| Repair by welding of pipe body plate, and skelp | Permitted | Prohibited |
| Repair by welding of weld seams without filler metal | Permitted by agreement | Prohibited |
Non-destructive inspection of a seamless pipe is mandatory for PSL2 pipe, whereas for PLS1 pipe, it is a supplementary requirement.
Repair of pipe body plate and skelp by welding is not allowed in PSL2 pipes, whereas it is allowed in PSL1 pipes. Similarly, weld repair without filler metal is not allowed in PSL2 pipes, whereas it is allowed with the purchaser’s permission in PSL1 pipes.
Certification & Traceability
| PARAMETER | PSL1 | PSL2 |
|---|---|---|
| Certification | Traceable only until all tests are passed | Certificates (SR15.1) mandatory |
| Traceability | Traceable only until all tests are passed unless SR15 is specified | Traceable after completion of tests (SR15.2) mandatory |
For PSL1 pipes, Traceability & Certification is not required beyond the point it passes all the required tests whereas, for PSL2 pipes, Traceability & Certification is mandatory.
In short PSL1 pipes are standard quality pipes for normal services, and PSL2 pipes are higher quality pipes than PSL1.
I hope you have enjoyed the video on what is the difference between PSL1 and PSL2 pipes. Don’t forget to subscribe to my channel to get regular updates on new videos and also like and share my video with your friends.
If you want to request a video, please write in the comment below. And don’t forget to check the free piping component guide by visiting my website hardhatengineer.com. See you soon, goodbye, take care.
Are You Piping Components Master?