In piping, a Gasket is sealing material placed between connecting flanges to create a static seal. This will maintain the leakage-proof sealing in all operating conditions. Different types of gaskets are used to achieve leakproof sealing between the pipe flange.
The primary function of gaskets is to seal the irregularities of each face of the flange so that there will be no leakage of the service fluid from the flange joint.
Types of Gaskets
There are three types of gaskets used in process piping.
- Non-Metallic
- Metallic
- Composite
| Non-Metallic | Metallic – Ring Gasket | Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Compressed Non-Asbestos Fibre Gasket (CNAF) | Oval Ring Gasket | Spiral Wound Gaskets |
| PTFE Gasket | Octagonal Ring Gasket | Camprofile Gaskets |
| Rubber Gasket | Metal Jacketed Gasket |
Non-Metallic Gasket
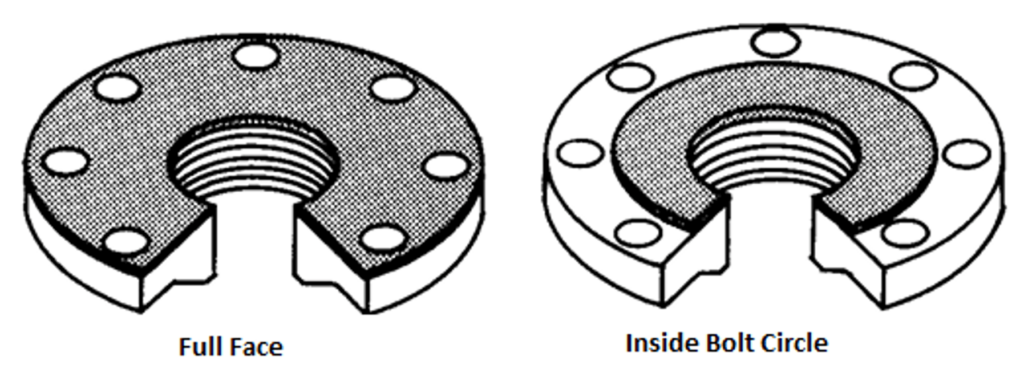
The most common materials used for this type of gaskets are Graphite, Rubber, Teflon, PTFE, and Compressed Non-Asbestos Fiber (CNAF). These gaskets are also known as soft gaskets. It can be full face or inside bolt circle type.
- Non-Metallic gaskets can easily compress with low tension bolting
- These types of gaskets are used with low-pressure class flanges such as 150 and 300 Class and also in low-temperature However, graphite gasket can be used up to 500 Degree centigrade.
- Rubber and elastomer gaskets are not used in hydrocarbon services but used in utility lines.
- Non-Metallic gaskets are the cheapest and most easily available
Full-face gasket types are suitable for flat-face (FF) flanges. Flat ring gasket types are suitable for use with raised-faced (RF) flanges.
You can see in the right-side image a full-face gasket, and the left side is inside the bolt circle gasket. The image also shows CNAF & PTFE gaskets. Full face gasket can only be used with FF flange and is normally used for temporary connection of utility lines.
Gasket Quiz – Test yourself, Take This Quiz
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
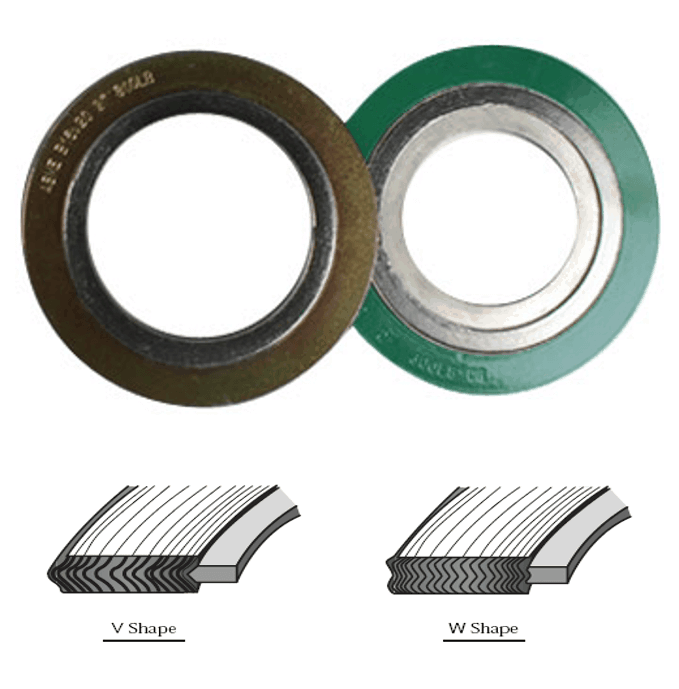
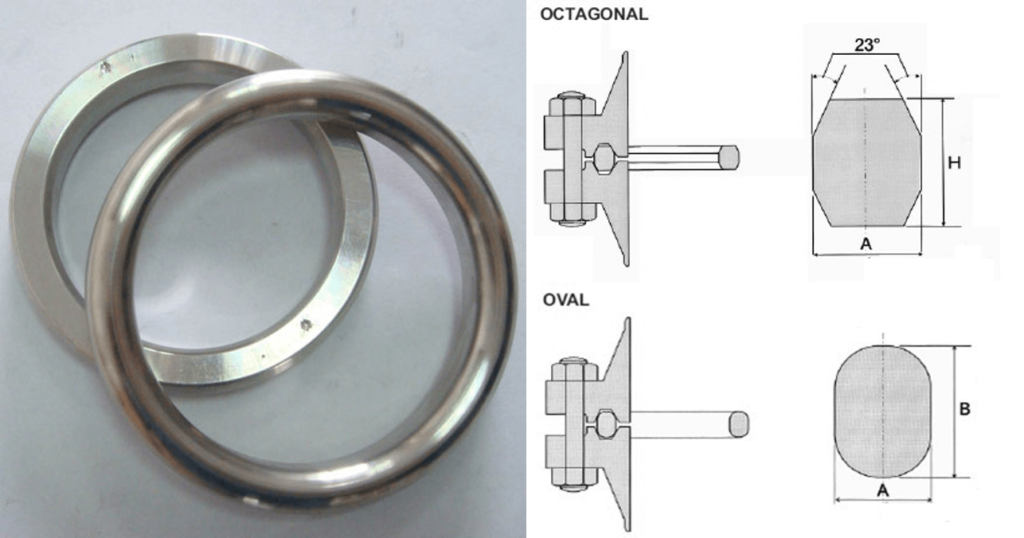
Metal Gasket / Ring Joint Gasket / RTJ Gasket
Metal gaskets are manufactured from a material such as Soft iron, Low Carbon steel, Stainless Steel, Monel, and Inconel. These gaskets are also known as ring gaskets or RTJ gaskets.
- Metallic gaskets are used in high-pressure class flanges, normally above 900 Class; they can also be used for high-temperature
- High tension bolting is required when we use metallic gaskets.
- They are very robust & most costly.
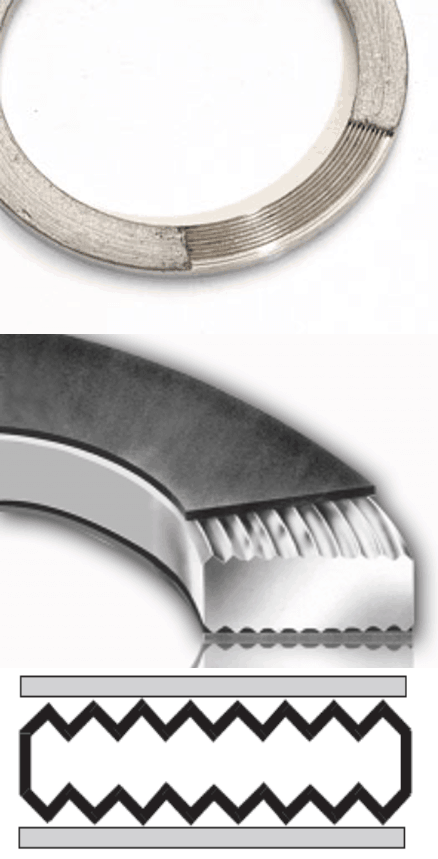
The RTJ Gasket fits in a groove machined on the flange face of both mating flanges. Two types of the metallic gasket are used with RTJ flange Octagonal and Oval. You can see the difference in their cross-section view.
Composite Gasket or Semi-Metallic
Composite gaskets are a combination of metal and non-metal materials. Different types of combinations of materials are possible based on the service requirement.
Spiral wound, Metal Jacketed, and Kamprofile gasket are well known in the composite gasket category. They are used in a wide range of pressure and temperature services.
Composite gaskets are cost-effective compared to metal gaskets, but Careful handling is required. Composite gaskets are used on raised faces, male-female, and tongue-and-groove flanges.
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
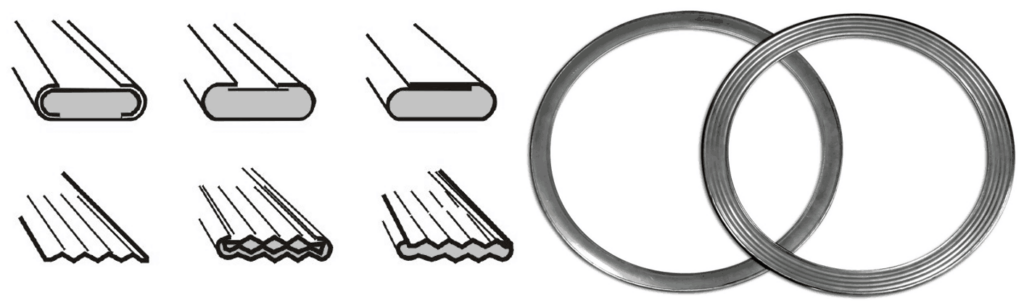
Spiral Wound Gasket
The most widely used composite type gasket is a Spiral Wound Gasket. It is suitable for a wide range of pressure and temperature class. Normally Graphite or PTFE is used as filler material & stainless steel or other exotic material is used as the winding material.
There are three components in the spiral wound gasket. Inner & Outer ring, filler material, and winding material. However, sometimes an inner ring is not used. You can see in the image a spiral wound gasket with and without an inner ring.
The inner ring is used to provide additional support to the winding material. The winding is an alternative layer of filler material and winding material. The filler material is a soft material such as graphite and PTFE, and the winding material is a thin sheet of metal.
Kammprofile / Campofile Gasket
Kamm/ Cam profile Gasket is having a solid metal core with concentric grooves. Filler material, either graphite or PTFE, is layered on this grooved metal ring. It is Costlier than the Spiral wound gasket but provides better blowout resistance and is easy to handle even in large diameters.
Kammprofile gaskets are used in a wide variety of service fluids and operating pressure-temperatures classes from Class 150 to Class 2500 flanges.
Metal Jacketed Gasket
In Metal Jacketed Gasket, the Soft filler material is enclosed in a thin sheet of a metal jacket. There are different ways to cover filler material, as shown in the image.
Jacketed gaskets are easily fabricated in a variety of sizes and shapes. They are used in heat exchangers, shells, channels, and cover flange joints. It is also used in valves’ body bonnet joints.
Why Gaskets are used?
A leak from the flange joint can be disastrous. A flange leak results in loss of product and energy. No plant operator wants to leak of toxic or hazardous material that can harm humans and the environment.
The gasket can help achieve reliable sealing to prevent flange joints’ leaks.
Types of Gaskets to be used in a given fluid service depend on the parameters, such as
- Temperature – Gasket material must withstand the entire design temperature range of the fluid it handles.
- Pressure – Gasket material must withstand the entire design pressure range of the fluid it handles.
- Corrosion resistance – Gasket material should not corrode when it comes in contact with the fluid it handles or by environmental exposure.
- Types of fluid – Gasket material should be capable of dealing with different types of fluids if installed in a line that handles more than one type of fluids.
- Robustness – The gasket must be capable of withstanding all movement that may occur due to temperature and pressure changes.
- Availability – The gasket should be easy.
- Cost – Cheap and unreliable gasket should not be used at the same time, it should not be costly.
Selection of Gasket
Proper selection of gasket depends upon the following factors.
- Compatibility of the gasket material with the fluid.
- Ability to withstand the pressure temperature of the system.
- The service life of the gasket
It is important to understand the requirements of particular applications before making gasket selection. Gaskets must maintain a seal for an acceptable period against all the operational forces involved.
There are eight important properties that any gasket must possess to achieve this –
- Impermeability – The gasket should not be porous to the fluid being sealed.
- Compressibility – The gasket should compress into the imperfections on the flange sealing faces to create the initial seal.
- Stress relaxation (creep resistance) – The gasket should not show significant flow (creep) when subjected to load and temperature. Such flow will allow the bolts to relax, reduce gasket surface stress, and cause leakage.
- Resilience – Although normally stable, flanges do, in fact, move slightly relative to one another under the influence of cycling temperature and pressure. The gasket should be capable of compensating for such movements.
- Chemical resistance – The gasket should withstand chemical attack from the process medium being handled. Likewise, the gasket material itself must not contaminate the process medium.
- Temperature resistance – The gasket should be able to withstand the effects of the maximum and minimum temperatures within the process and the external atmospheric temperatures.
- Anti-stick – The gasket has to be easily removable after use.
- Anti-corrosion – The gasket must not cause corrosion of the flange faces.
Unlock New Skills with Our Best Selling Online Courses
Gasket Materials
Non-Metallic Gasket is manufactured from flexible materials. Such as
- Compressed Non-Asbestos fiber
- PTFE
- Rubber
- Mica
- And Ceramic fiber
A list of materials that can be used for metallic gaskets is given in ASME B16.20. Some of the materials are
- Soft iron
- Low carbon steel
- 4-6% Chrome, ½ Mo
- Stainless steel Type 304,316,347,410
- Or metallic gasket can be manufactured from Service specific material as suggested by the designer.
The only thing you have to take care of is that the hardness of the gasket shall always be less than flange material by at least 50 BHN.
What will happen if gasket hardness is more than flange? When you tighten the flange, the gasket will damage the serration and will no longer hold the leak.
Winding and Outer Ring Materials Types
In a spiral wound gasket, Winding Strips are manufactured from
- Stainless steel material grades such as Type 304,316,347
- Or Exotic material such as Monel, titanium, or a duplex can also be used as per service requirements.
The filler material of the winding can be a Flexible Graphite or PTFE, depending on of service temperature of gaskets. PTFE is not used for high-temperature services.
The Outer Ring of the Spiral Wound Gasket is mostly manufactured from Carbon steel, whereas the Inner ring is mostly manufactured from Stainless Steel Type 304,316,321,347.
It can also be manufactured from exotic materials such as monel, titanium, duplex, etc. These depend on the type of fluid inside the pipe as an inner ring is in direct contact with the fluid.
Cammprofile and metal jacketed gaskets are manufactured from the same materials used to manufacture Spiral Wound Gasket.
Dimensional Standards
Gasket dimensions are covered in the following standards.
- BS 3381 – Metallic Spiral Wound Gaskets
- ASME B 16.20 -Metallic Gaskets for pipe flanges
- ASME B 16.21-Non-metallic Gaskets for pipe flanges.
Learn more on gasket – flexitallic, Lamons
Are You Piping Components Master?